Traffic Control for Railroad and Light Rail Transit Grade Crossings
Section 8D.01 Purpose
Support:
01 Traffic control for pathway grade crossings includes all signs, signals, markings, other warning devices, and their supports at pathway grade crossings and along pathway approaches to grade crossings. The function of this traffic control is to promote safety and provide effective operation of both rail and pathway traffic at pathway grade crossings.
02 Except as specifically provided in this Chapter, sidewalks are considered to be part of a highway-rail or highway-LRT grade crossing rather than a pathway grade crossing, and are covered by the provisions of Chapters 8B and 8C rather than by the provisions of this Chapter. However, many of the treatments outlined in this Chapter are applicable to sidewalks adjacent to highway-rail or highway-LRT grade crossings, including detectable warnings, swing gates, and automatic gates.
03 Crosswalks at intersections where pedestrians cross LRT tracks in mixed-use alignments are covered by the provisions of Section 3B.18 rather than by the provisions of this Chapter.
Section 8D.02 Use of Standard Devices, Systems, and Practices
Guidance:
01 The public agency with jurisdiction over the pathway and the regulatory agency with statutory authority, if applicable, should jointly determine the need and selection of devices at a pathway grade crossing, including the appropriate traffic control system to be used.
Section 8D.03 Pathway Grade Crossing Signs and Markings
Standard:
01 Pathway grade crossing signs shall be standard in shape, legend, and color.
02 Traffic control devices mounted adjacent to pathways at a height of less than 8 feet measured vertically from the bottom edge of the device to the elevation of the near edge of the pathway surface shall have a minimum lateral offset of 2 feet from the near edge of the device to the near edge of the pathway (see Figure 9B-1).
03 The minimum mounting height for post-mounted signs on pathways shall be 4 feet, measured vertically from the bottom edge of the sign to the elevation of the near edge of the pathway surface (see Figure 9B-1).
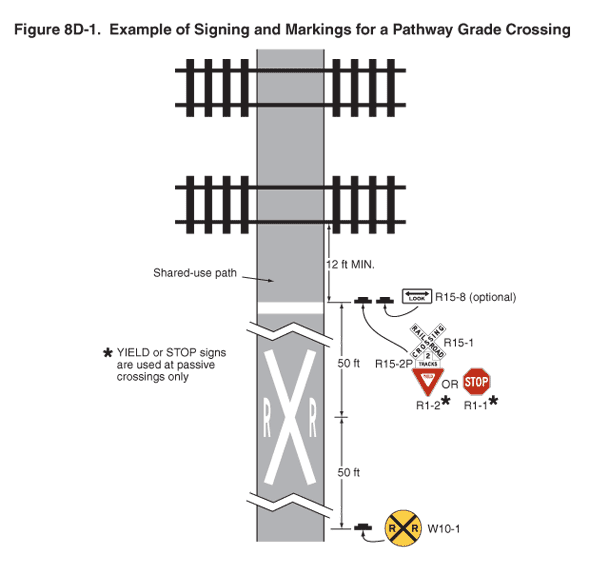
04 Pathway grade crossing traffic control devices shall be located a minimum of 12 feet from the center of the nearest track.
05 The minimum sizes of pathway grade crossing signs shall be as shown in the shared-use path column in Table 9B-1.
06 When overhead traffic control devices are used on pathways, the clearance from the bottom edge of the device to the pathway surface directly under the sign or device shall be at least 8 feet.
Guidance:
07 If pathway users include those who travel faster than pedestrians, such as bicyclists or skaters, the use of warning signs and pavement markings in advance of the pathway grade crossing (see Figure 8D-1) should be considered.
Figure 8D-1 Example of Signing and Markings for a Pathway Grade Crossing
Section 8D.04 Stop Lines, Edge Lines, and Detectable Warnings
Guidance:
01 If used at pathway grade crossings, the pathway stop line should be a transverse line at the point where a pathway user is to stop. The pathway stop line should be placed at least 2 feet further from the nearest rail than the gate, counterweight, or flashing-light signals (if any of these are present) is placed, and at least 12 feet from the nearest rail.
Option:
02 Edge lines (see Section 3B.06) may be used on approach to and across the tracks at a pathway grade crossing, a sidewalk at a highway-rail or highway-LRT grade crossing, or a station crossing to delineate the designated pathway user route.
Support:
03 Edge line delineation can be beneficial where the distance across the tracks is long, commonly because of a skewed grade crossing or because of multiple tracks, or where the pathway surface is immediately adjacent to a traveled way.
04 Detectable warning surfaces (see Section 3B.18) that contrast visually with adjacent walking surfaces, either light-on-dark or dark-on-light, can be used to warn pedestrians about the locations of the tracks at a grade crossing. The "Americans with Disabilities Act Accessibility Guidelines for Buildings and Facilities (ADAAG)" (see Section 1A.11) contains specifications for design and placement of detectable warning surfaces.
Section 8D.05 Passive Devices for Pathway Grade Crossings
Standard:
01 Except as provided in Paragraph 2, where active traffic control devices are not used, a Crossbuck Assembly shall be installed on each approach to a pathway grade crossing.
Option:
02 The Crossbuck Assembly may be omitted at station crossings and on the approaches to a pathway grade crossing that is located within 25 feet of the traveled way at a highway-rail or highway-LRT grade crossing.
Guidance:
03 The pathway user's ability to detect the presence of approaching rail traffic should be considered in determining the type and placement of traffic control devices or design features (such as fencing or swing gates).
04 Nighttime visibility should be considered if design features (such as fencing or swing gates) are used to channelize pathway users.
05 If automatic gates and swing gates are used, the pathway should be channelized to direct users to the entrance to and exit from the pathway grade crossing.
Standard:
06 If used, swing gates shall be designed to open away from the track(s) so that pathway users can quickly push the gate open when moving away from the track(s). If used, swing gates shall be designed to automatically return to the closed position after each use.
Option:
07 When used in conjunction with automatic gates at pathway grade crossings, swing gates may be equipped with a latching device that permits the gate to be opened only from the track side of the gate.
Support:
08 The "Americans with Disabilities Act Accessibility Guidelines for Buildings and Facilities (ADAAG)" (see Section 1A.11) contains information regarding spring hinges and door and gate opening forces for swing gates.
Section 8D.06 Active Traffic Control Systems for Pathway Grade Crossings
Standard:
01 If used at a pathway grade crossing, an active traffic control system shall include flashing-light signals for each direction of the pathway. A bell or other audible warning device shall also be provided.
Option:
02 Separate active traffic control devices may be omitted at a pathway grade crossing that is located within 25 feet of the traveled way of a highway-rail or highway-LRT grade crossing that is equipped with an active traffic control system.
Standard:
03 If used at pathway grade crossings, alternately flashing red lights shall be aligned horizontally and the light units shall have a diameter of at least 4 inches. The minimum mounting height of the flashing red lights shall be 4 feet, measured vertically from the bottom edge of the lights to the elevation of the near edge of the pathway surface.
Option:
04 Traffic control devices may be installed between the tracks at multiple track crossings at stations.
Standard:
05 The mounting height for flashing lights that are installed between the tracks at multiple track crossings at stations shall be a minimum of 1 foot, measured vertically from the bottom edge of the lights to the elevation of the near edge of the pathway surface.
Option:
06 Automatic gates may be used at pathway grade crossings.
Guidance:
07 If used at a pathway grade crossing, the height of the automatic gate arm when in the down position should be a minimum of 2.5 feet and a maximum of 4 feet above the sidewalk.
08 If used, the gate configuration, which might include a combination of automatic gates and swing gates, should provide for full width coverage of the pathway on both approaches to the track.
Standard:
09 Where a sidewalk is located between the edge of a roadway and the support for a gate arm that extends across the sidewalk and into the roadway, the location, placement, and height prescribed for vehicular gates shall be used (see Section 8C.04).
Guidance:
10 If a separate automatic gate is used for a sidewalk, the height of the gate arm when in the down position should be a minimum of 2.5 feet and a maximum of 4 feet above the sidewalk.
11 If a separate automatic gate is used for a sidewalk at a highway-rail or highway-LRT grade crossing, instead of a supplemental or auxiliary gate arm installed as a part of the same mechanism as the vehicular gate, a separate mechanism should be provided for the sidewalk gate to prevent a pedestrian from raising the vehicular gate.
