Temporary Traffic Control
Section 6F.01 Types of Devices
Guidance:
01 The design and application of TTC devices used in TTC zones should consider the needs of all road users (motorists, bicyclists, and pedestrians), including those with disabilities.
Support:
02 FHWA policy requires that all roadside appurtenances such as traffic barriers, barrier terminals and crash cushions, bridge railings, sign and light pole supports, and work zone hardware used on the National Highway System meet the crashworthy performance criteria contained in the National Cooperative Highway Research Program (NCHRP) Report 350, "Recommended Procedures for the Safety Performance Evaluation of Highway Features." The FHWA website at "http://safety.fhwa.dot.gov/programs/roadside_hardware.jsp" identifies all such hardware and includes copies of FHWA acceptance letters for each of them. In the case of proprietary items, links are provided to manufacturers' websites as a source of detailed information on specific devices. The website also contains an "Ask the Experts" section where questions on roadside design issues can be addressed.
03 Various Sections of the MUTCD require certain traffic control devices, their supports, and/or related appurtenances to be crashworthy. Such MUTCD crashworthiness provisions apply to all streets, highways, and private roads open to public travel. Also, State Departments of Transportation and local agencies might have expanded the NCHRP Report 350 crashworthy criteria to apply to certain other roadside appurtenances.
04 Crashworthiness and crash testing information on devices described in Part 6 are found in AASHTO's "Roadside Design Guide" (see Section 1A.11).
05 As defined in Section 1A.13, "crashworthy" is a characteristic of a roadside appurtenance that has been successfully crash tested in accordance with a national standard such as the NCHRP Report 350, "Recommended Procedures for the Safety Performance Evaluation of Highway Features."
Standard:
06 Traffic control devices shall be defined as all signs, signals, markings, and other devices used to regulate, warn, or guide road users, placed on, over, or adjacent to a street, highway, private roads open to public travel (see definition in Section 1A.13), pedestrian facility, or bikeway by authority of a public body or official having jurisdiction.
07 All traffic control devices used for construction, maintenance, utility, or incident management operations on a street, highway, or private road open to public travel (see definition in Section 1A.13) shall comply with the applicable provisions of this Manual.
Section 6F.02 General Characteristics of Signs
Support:
01 TTC zone signs convey both general and specific messages by means of words, symbols, and/or arrows and have the same three categories as all road user signs: regulatory, warning, and guide.
Standard:
02 The colors for regulatory signs shall follow the Standards for regulatory signs in Table 2A-5 and Chapter 2B. Warning signs in TTC zones shall have a black legend and border on an orange background, except for the Grade Crossing Advance Warning (W10-1) sign which shall have a black legend and border on a yellow background, and except for signs that are required or recommended in Parts 2 or 7 to have fluorescent yellow-green backgrounds. Colors for guide signs shall follow the Standards in Table 2A-5 and Chapter 2D, except for guide signs as otherwise provided in Section 6F.55.
Option:
03 Where the color orange is required, the fluorescent orange color may also be used.
Support:
04 The fluorescent version of orange provides higher conspicuity than standard orange, especially during twilight.
Option:
05 Existing warning signs that are still applicable may remain in place.
06 In order to maintain the systematic use of yellow or fluorescent yellow-green backgrounds for pedestrian, bicycle, and school warning signs in a jurisdiction, the yellow or fluorescent yellow-green background for pedestrian, bicycle, and school warning signs may be used in TTC zones.
07 Standard orange flags or flashing warning lights may be used in conjunction with signs.
Standard:
08 When standard orange flags or flashing warning lights are used in conjunction with signs, they shall not block the sign face.
09 Except as provided in Section 2A.11, the sizes for TTC signs and plaques shall be as shown in Table 6F-1. The sizes in the minimum column shall only be used on local streets or roadways where the 85th-percentile speed or posted speed limit is less than 35 mph.
| Sign or Plaque | Sign Designation | Section | Conventional Road | Freeway or Expressway | Minimum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stop | R1-1 | 6F.06 | 30 x 30* | — | — |
| Stop (on Stop/Slow Paddle) | R1-1 | 6E.03 | 18 x 18 | — | — |
| Yield | R1-2 | 6F.06 | 36 x 36 x 36* | 48 x 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 x 30 |
| To Oncoming Traffic (plaque) | R1-2aP | 6F.06 | 36 x 30 | 48 x 36 | 24 x 18 |
| Wait on Stop | R1-7 | 6E.05 | 24 x 30 | 24 x 30 | — |
| Go on Slow | R1-8 | 6E.05 | 24 x 30 | 24 x 30 | — |
| Speed Limit | R2-1 | 6F.12 | 24 x 30* | 36 x 48 | — |
| Fines Higher (plaque) | R2-6P | 6F.12 | 24 x 18 | 36 x 24 | — |
| Fines Double (plaque) | R2-6aP | 6F.12 | 24 x 18 | 36 x 24 | — |
| $XX Fine (plaque) | R2-6bP | 6F.12 | 24 x 18 | 36 x 24 | — |
| Begin Higher Fines Zone | R2-10 | 6F.12 | 24 x 30 | 36 x 48 | — |
| End Higher Fines Zone | R2-11 | 6F.12 | 24 x 30 | 36 x 48 | — |
| End Work Zone Speed Limit | R2-12 | 6F.12 | 24 x 36 | 36 x 54 | — |
| Movement Prohibition | R3-1,2,3,4,18,27 | 6F.06 | 24 x 24* | 36 x 36 | — |
| Mandatory Movement (1 lane) | R3-5 | 6F.06 | 30 x 36 | — | — |
| Optional Movement (1 lane) | R3-6 | 6F.06 | 30 x 36 | — | — |
| Mandatory Movement (text) | R3-7 | 6F.06 | 30 x 30* | — | — |
| Advance Intersection Lane Control | R3-8 | 6F.06 | Varies x 30 | — | — |
| Do Not Pass | R4-1 | 6F.06 | 24 x 30 | 36 x 48 | — |
| Pass With Care | R4-2 | 6F.06 | 24 x 30 | 36 x 48 | — |
| Keep Right | R4-7 | 6F.06 | 24 x 30 | 36 x 48 | — |
| Narrow Keep Right | R4-7c | 6F.06 | 18 x 30 | — | — |
| Stay in Lane | R4-9 | 6F.11 | 24 x 30 | 36 x 48 | — |
| Do Not Enter | R5-1 | 6F.06 | 30 x 30* | 36 x 36 | — |
| Wrong Way | R5-1a | 6F.06 | 36 x 24* | 42 x 30 | — |
| One Way | R6-1 | 6F.06 | 36 x 12* | 54 x 18 | — |
| One Way | R6-2 | 6F.06 | 24 x 30* | 36 x 48 | — |
| No Parking (symbol) | R8-3 | 6F.06 | 24 x 24 | 36 x 36 | — |
| Pedestrian Crosswalk | R9-8 | 6F.13 | 36 x 18 | — | — |
| Sidewalk Closed | R9-9 | 6F.14 | 24 x 12 | — | — |
| Sidewalk Closed, Use Other Side | R9-10 | 6F.14 | 24 x 12 | — | — |
| Sidewalk Closed Ahead, Cross Here | R9-11 | 6F.14 | 24 x 18 | — | — |
| Sidewalk Closed, Cross Here | R9-11a | 6F.14 | 24 x 12 | — | — |
| Road Closed | R11-2 | 6F.08 | 48 x 30 | — | — |
| Road Closed - Local Traffic Only | R11-3a,3b,4 | 6F.09 | 60 x 30 | — | — |
| Weight Limit | R12-1,2 | 6F.10 | 24 x 30 | 36 x 48 | — |
| Weight Limit (with symbols) | R12-5 | 6F.10 | 24 x 36 | 36 x 48 | — |
| Turn and Curve Signs | W1-1,2,3,4 | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Reverse Curve (2 or more lanes) | W1-4b,4c | 6F.48 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| One-Direction Large Arrow | W1-6 | 6F.16 | 48 x 24 | 60 x 30 | — |
| Chevron | W1-8 | 6F.16 | 18 x 24 | 30 x 36 | — |
| Stop Ahead | W3-1 | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Yield Ahead | W3-2 | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Signal Ahead | W3-3 | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Be Prepared to Stop | W3-4 | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Reduced Speed Limit Ahead | W3-5 | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| XX MPH Speed Zone Ahead | W3-5a | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Merging Traffic | W4-1,5 | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 36 x 36 |
| Lane Ends | W4-2 | 6F.24 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Added Lane | W4-3,6 | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| No Merge Area (plaque) | W4-5P | 6F.16 | 18 x 24 | 24 x 30 | — |
| Road Narrows | W5-1 | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Narrow Bridge | W5-2 | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| One Lane Bridge | W5-3 | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Ramp Narrows | W5-4 | 6F.26 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Divided Highway | W6-1 | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Divided Highway Ends | W6-2 | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Two-Way Traffic | W6-3 | 6F.32 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Two-Way Traffic | W6-4 | 6F.76 | 12 x 18 | 12 x 18 | — |
| Hill (symbol) | W7-1 | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Next XX Miles (plaque) | W7-3aP | 6F.53 | 24 x 18 | 36 x 30 | — |
| Bump | W8-1 | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Dip | W8-2 | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Pavement Ends | W8-3 | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Soft Shoulder | W8-4 | 6F.44 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Slippery When Wet | W8-5 | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Truck Crossing | W8-6 | 6F.36 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Loose Gravel | W8-7 | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Rough Road | W8-8 | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Low Shoulder | W8-9 | 6F.44 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Uneven Lanes | W8-11 | 6F.45 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| No Center Line | W8-12 | 6F.47 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Fallen Rocks | W8-14 | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Grooved Pavement | W8-15 | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Motorcycle (plaque) | W8-15P | 6F.54 | 24 x 18 | 30 x 24 | — |
| Shoulder Drop Off (symbol) | W8-17 | 6F.44 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Shoulder Drop-Off (plaque) | W8-17P | 6F.44 | 24 x 18 | 30 x 24 | — |
| Road May Flood | W8-18 | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 24 x 24 |
| No Shoulder | W8-23 | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Steel Plate Ahead | W8-24 | 6F.46 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Shoulder Ends | W8-25 | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Lane Ends | W9-1,2 | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Center Lane Closed Ahead | W9-3 | 6F.23 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Grade Crossing Advance Warning | W10-1 | 6F.16 | 36 dia. | — | — |
| Truck | W11-10 | 6F.36 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Double Arrow | W12-1 | 6F.16 | 30 x 30 | — | — |
| Low Clearance | W12-2 | 6F.16 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Advisory Speed (plaque) | W13-1P | 6F.52 | 24 x 24 | 30 x 30 | 18 x 18 |
| On Ramp (plaque) | W13-4P | 6F.25 | 36 x 36 | 36 x 36 | — |
| No Passing Zone (pennant) | W14-3 | 6F.16 | 48 x 48 x 36 | 64 x 64 x 48 | 40 x 40 x 30 |
| XX Feet (plaque) | W16-2P | 6F.16 | 24 x 18 | 30 x 24 | — |
| Road Work (with distance) | W20-1 | 6F.18 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Detour (with distance) | W20-2 | 6F.19 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Road (Street) Closed (with distance) | W20-3 | 6F.20 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| One Lane Road (with distance) | W20-4 | 6F.21 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Lane(s) Closed (with distance) | W20-5,5a | 6F.22 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Flagger (symbol) | W20-7 | 6F.31 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Flagger | W20-7a | 6F.31 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Slow (on Stop/Slow Paddle) | W20-8 | 6E.03 | 18 x 18 | — | — |
| Workers | W21-1,1a | 6F.33 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Fresh Oil (Tar) | W21-2 | 6F.34 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Road Machinery Ahead | W21-3 | 6F.35 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Slow Moving Vehicle | W21-4 | 6G.06 | 36 x 18 | — | — |
| Shoulder Work | W21-5 | 6F.37 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Shoulder Closed | W21-5a | 6F.37 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Shoulder Closed (with distance) | W21-5b | 6F.37 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Survey Crew | W21-6 | 6F.38 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Utility Work Ahead | W21-7 | 6F.39 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Mowing Ahead | W21-8 | 6G.06 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Blasting Zone Ahead | W22-1 | 6F.41 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Turn Off 2-Way Radio and Cell Phone | W22-2 | 6F.42 | 42 x 36 | 42 x 36 | — |
| End Blasting Zone | W22-3 | 6F.43 | 42 x 36 | 42 x 36 | 36 x 30 |
| Slow Traffic Ahead | W23-1 | 6F.27 | 48 x 24 | 48 x 24 | — |
| New Traffic Pattern Ahead | W23-2 | 6F.30 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Double Reverse Curve (1 lane) | W24-1 | 6F.49 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Double Reverse Curve (2 lanes) | W24-1a | 6F.49 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| Double Reverse Curve (3 lanes) | W24-1b | 6F.49 | 36 x 36 | 48 x 48 | 30 x 30 |
| All Lanes | W24-1cP | 6F.49 | 24 x 24 | 30 x 30 | — |
| Road Work Next XX Miles | G20-1 | 6F.56 | 36 x 18 | 48 x 24 | — |
| End Road Work | G20-2 | 6F.57 | 36 x 18 | 48 x 24 | — |
| Pilot Car Follow Me | G20-4 | 6F.58 | 36 x 18 | — | — |
| Work Zone (plaque) | G20-5aP | 6F.12 | 24 x 18 | 36 x 24 | — |
| Exit Open | E5-2 | 6F.28 | 48 x 36 | 48 x 36 | — |
| Exit Closed | E5-2a | 6F.28 | 48 x 36 | 48 x 36 | — |
| Exit Only | E5-3 | 6F.29 | 48 x 36 | 48 x 36 | — |
| Detour | M4-8 | 6F.59 | 24 x 12 | 30 x 15 | — |
| End Detour | M4-8a | 6F.59 | 24 x 18 | 24 x 18 | — |
| End | M4-8b | 6F.59 | 24 x 12 | 24 x 12 | — |
| Detour | M4-9 | 6F.59 | 30 x 24 | 48 x 36 | — |
| Bike/Pedestrian Detour | M4-9a | 6F.59 | 30 x 24 | — | — |
| Pedestrian Detour | M4-9b | 6F.59 | 30 x 24 | — | — |
| Bike Detour | M4-9c | 6F.59 | 30 x 24 | — | — |
| Detour | M4-10 | 6F.59 | 48 x 18 | — | — |
* See Table 2B-1 for minimum size required for signs facing traffic on multi-lane conventional roads
Notes:
- Larger signs may be used wherever necessary for greater legibility or emphasis.
- Dimensions are shown in inches and are shown as width x height.
Option:
10 The dimensions of signs and plaques shown in Table 6F-1 may be increased wherever necessary for greater legibility or emphasis.
Standard:
11 Deviations from standard sizes as prescribed in this Manual shall be in 6-inch increments.
Support:
12 Sign design details are contained in the "Standard Highway Signs and Markings" book (see Section 1A.11).
13 Section 2A.06 contains additional information regarding the design of signs, including an Option allowing the development of special word message signs if a standard word message or symbol sign is not available to convey the necessary regulatory, warning, or guidance information.
Standard:
14 All signs used at night shall be either retroreflective with a material that has a smooth, sealed outer surface or illuminated to show the same shape and similar color both day and night.
15 The requirement for sign illumination shall not be considered to be satisfied by street, highway, or strobe lighting.
Option:
16 Sign illumination may be either internal or external.
17 Signs may be made of rigid or flexible material.
Section 6F.03 Sign Placement
Guidance:
01 Signs should be located on the right-hand side of the roadway unless otherwise provided in this Manual.
Option:
02 Where special emphasis is needed, signs may be placed on both the left-hand and right-hand sides of the roadway. Signs mounted on portable supports may be placed within the roadway itself. Signs may also be mounted on or above barricades.
Support:
03 The provisions of this Section regarding mounting height apply unless otherwise provided for a particular sign elsewhere in this Manual.
Standard:
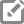
04 The minimum height, measured vertically from the bottom of the sign to the elevation of the near edge of the pavement, of signs installed at the side of the road in rural areas shall be 5 feet (see Figure 6F-1).
Figure 6F-1 Height and Lateral Location of Signs—Typical Installations
05 The minimum height, measured vertically from the bottom of the sign to the top of the curb, or in the absence of curb, measured vertically from the bottom of the sign to the elevation of the near edge of the traveled way, of signs installed at the side of the road in business, commercial, or residential areas where parking or pedestrian movements are likely to occur, or where the view of the sign might be obstructed, shall be 7 feet (see Figure 6F-1).
06 The minimum height, measured vertically from the bottom of the sign to the sidewalk, of signs installed above sidewalks shall be 7 feet.
Option:
07 The height to the bottom of a secondary sign mounted below another sign may be 1 foot less than the height provided in Paragraphs 4 through 6.
Guidance:
08 Neither portable nor permanent sign supports should be located on sidewalks, bicycle facilities, or areas designated for pedestrian or bicycle traffic. If the bottom of a secondary sign that is mounted below another sign is mounted lower than 7 feet above a pedestrian sidewalk or pathway (see Section 6D.02), the secondary sign should not project more than 4 inches into the pedestrian facility.
Standard:
09 Where it has been determined that the accommodation of pedestrians with disabilities is necessary, signs shall be mounted and placed in accordance with Section 4.4 of the "Americans with Disabilities Act Accessibility Guidelines for Buildings and Facilities (ADAAG)" (see Section 1A.11).
10 Signs mounted on barricades and barricade/sign combinations shall be crashworthy.
Guidance:
11 Except as provided in Paragraph 12, signs mounted on portable sign supports that do not meet the minimum mounting heights provided in Paragraphs 4 through 6 should not be used for a duration of more than 3 days.
Option:
12 The R9-8 through R9-11a series, R11 series, W1-6 through W1-8 series, M4-10, E5-1, or other similar type signs (see Figures 6F-3, 6F-4, and 6F-5) may be used on portable sign supports that do not meet the minimum mounting heights provided in Paragraphs 4 through 6 for longer than 3 days.
Support:
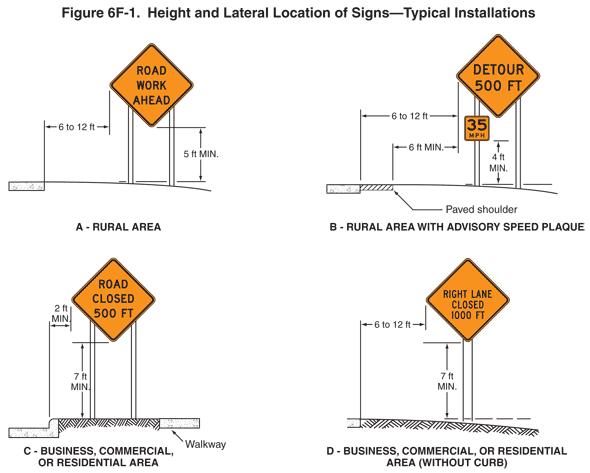
13 Methods of mounting signs other than on posts are illustrated in Figure 6F-2.
Figure 6F-2 Methods of Mounting Signs Other Than on Posts
Guidance:
14 Signs mounted on Type 3 Barricades should not cover more than 50 percent of the top two rails or 33 percent of the total area of the three rails.
Standard:
15 Sign supports shall be crashworthy. Where large signs having an area exceeding 50 square feet are installed on multiple breakaway posts, the clearance from the ground to the bottom of the sign shall be at least 7 feet.
16 The bottom of a sign mounted on a barricade, or other portable support, shall be at least 1 foot above the traveled way.
Option:
17 For mobile operations, a sign may be mounted on a work vehicle, a shadow vehicle, or a trailer stationed in advance of the TTC zone or moving along with it.
Support:
18 If alterations are made to specific traffic control device supports that have been successfully crash tested in accordance with NCHRP Report 350, the altered supports might not be considered to be crashworthy.
Section 6F.04 Sign Maintenance
Guidance:
01 Signs should be properly maintained for cleanliness, visibility, and correct positioning.
02 Signs that have lost significant legibility should be promptly replaced.
Support:
03 Section 2A.08 contains information regarding the retroreflectivity of signs, including the signs that are used in TTC zones.
Section 6F.05 Regulatory Sign Authority
Support:
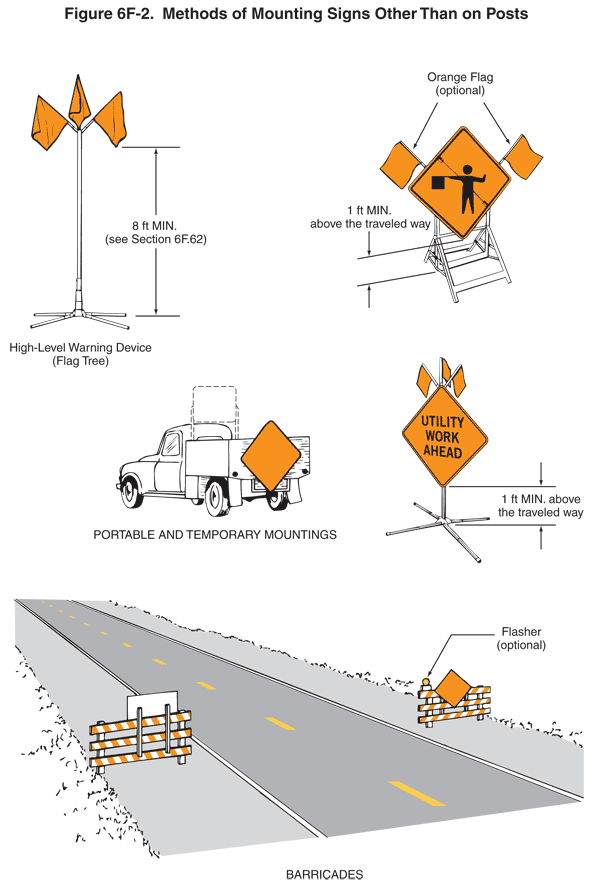
01 Regulatory signs such as those shown in Figure 6F-3 inform road users of traffic laws or regulations and indicate the applicability of legal requirements that would not otherwise be apparent.
Figure 6F-3 Regulatory Signs and Plaques in Temporary Traffic Control Zones
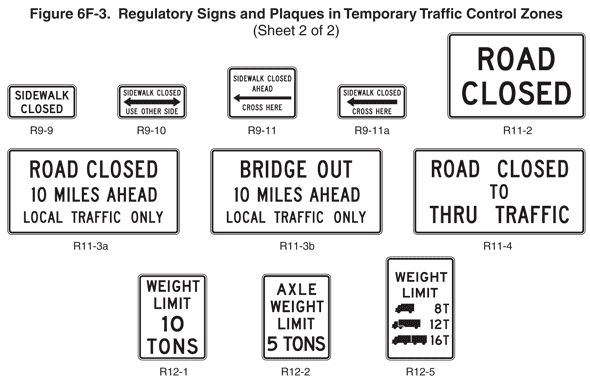
Standard:
02 Regulatory signs shall be authorized by the public agency or official having jurisdiction and shall conform with Chapter 2B.
Section 6F.06 Regulatory Sign Design
Standard:
01 TTC regulatory signs shall comply with the Standards for regulatory signs presented in Part 2 and in the FHWA's "Standard Highway Signs and Markings" book (see Section 1A.11).
Support:
02 Regulatory signs are generally rectangular with a black legend and border on a white background. Exceptions include the STOP, YIELD, DO NOT ENTER, WRONG WAY, and ONE WAY signs.
Option:
03 The ONE WAY sign may be either a horizontal or vertical rectangular sign.
Section 6F.07 Regulatory Sign Applications
Standard:
01 If a TTC zone requires regulatory measures different from those existing, the existing permanent regulatory devices shall be removed or covered and superseded by the appropriate temporary regulatory signs. This change shall be made in compliance with applicable ordinances or statutes of the jurisdiction.
Section 6F.08 ROAD (STREET) CLOSED Sign (R11-2)
Guidance:
01 The ROAD (STREET) CLOSED (R11-2) sign (see Figure 6F-3) should be used when the roadway is closed to all road users except contractors' equipment or officially authorized vehicles. The R11-2 sign should be accompanied by appropriate warning and detour signing.
Option:
02 The words BRIDGE OUT (or BRIDGE CLOSED) may be substituted for ROAD (STREET) CLOSED where applicable.
Guidance:
03 The ROAD (STREET) CLOSED sign should be installed at or near the center of the roadway on or above a Type 3 Barricade that closes the roadway (see Section 6F.68).
Standard:
04 The ROAD (STREET) CLOSED sign shall not be used where road user flow is maintained through the TTC zone with a reduced number of lanes on the existing roadway or where the actual closure is some distance beyond the sign.
Section 6F.09 Local Traffic Only Signs (R11-3a, R11-4)
Guidance:
01 The Local Traffic Only signs (see Figure 6F-3) should be used where road user flow detours to avoid a closure some distance beyond the sign, but where local road users can use the roadway to the point of closure. These signs should be accompanied by appropriate warning and detour signing.
02 In rural applications, the Local Traffic Only sign should have the legend ROAD CLOSED XX MILES AHEAD, LOCAL TRAFFIC ONLY (R11-3a).
Option:
03 In urban areas, the legend ROAD (STREET) CLOSED TO THRU TRAFFIC (R11-4) or ROAD CLOSED, LOCAL TRAFFIC ONLY may be used.
04 In urban areas, a word message that includes the name of an intersecting street name or well-known destination may be substituted for the words XX MILES AHEAD on the R11-3a sign where applicable.
05 The words BRIDGE OUT (or BRIDGE CLOSED) may be substituted for the words ROAD (STREET) CLOSED on the R11-3a or R11-4 sign where applicable.
Section 6F.10 Weight Limit Signs (R12-1, R12-2, R12-5)
Standard:
01 A Weight Limit sign (see Figure 6F-3), which shows the gross weight or axle weight that is permitted on the roadway or bridge, shall be consistent with State or local regulations and shall not be installed without the approval of the authority having jurisdiction over the highway.
02 When weight restrictions are imposed because of the activity in a TTC zone, a marked detour shall be provided for vehicles weighing more than the posted limit.
Section 6F.11 STAY IN LANE Sign (R4-9)
Option:
01 A STAY IN LANE (R4-9) sign (see Figure 6F-3) may be used where a multi-lane shift has been incorporated as part of the TTC on a highway to direct road users around road work that occupies part of the roadway on a multi-lane highway.
Section 6F.12 Work Zone and Higher Fines Signs and Plaques
Option:
01 A WORK ZONE (G20-5aP) plaque (see Figure 6F-3) may be mounted above a Speed Limit sign to emphasize that a reduced speed limit is in effect within a TTC zone. An END WORK ZONE SPEED LIMIT (R2-12) sign (see Figure 6F-3) may be installed at the downstream end of the reduced speed limit zone.
Guidance:
02 A BEGIN HIGHER FINES ZONE (R2-10) sign (see Figure 6F-3) should be installed at the upstream end of a work zone where increased fines are imposed for traffic violations, and an END HIGHER FINES ZONE (R2-11) sign (see Figure 6F-3) should be installed at the downstream end of the work zone.
Option:
03 Alternate legends such as BEGIN (or END) DOUBLE FINES ZONE may also be used for the R2-10 and R2-11 signs.
04 A FINES HIGHER, FINES DOUBLE, or $XX FINE plaque (see Section 2B.17 and Figure 6F-3) may be mounted below the Speed Limit sign if increased fines are imposed for traffic violations within the TTC zone.
05 Individual signs and plaques for work zone speed limits and higher fines may be combined into a single sign or may be displayed as an assembly of signs and plaques.
Section 6F.13 PEDESTRIAN CROSSWALK Sign (R9-8)
Option:
01 The PEDESTRIAN CROSSWALK (R9-8) sign (see Figure 6F-3) may be used to indicate where a temporary crosswalk has been established.
Standard:
02 If a temporary crosswalk is established, it shall be accessible to pedestrians with disabilities in accordance with Section 6D.02.
Section 6F.14 SIDEWALK CLOSED Signs (R9-9, R9-10, R9-11, R9-11a)
Guidance:
01 SIDEWALK CLOSED signs (see Figure 6F-3) should be used where pedestrian flow is restricted. Bicycle/Pedestrian Detour (M4-9a) signs or Pedestrian Detour (M4-9b) signs should be used where pedestrian flow is rerouted (see Section 6F.59).
02 The SIDEWALK CLOSED (R9-9) sign should be installed at the beginning of the closed sidewalk, at the intersections preceding the closed sidewalk, and elsewhere along the closed sidewalk as needed.
03 The SIDEWALK CLOSED, (ARROW) USE OTHER SIDE (R9-10) sign should be installed at the beginning of the restricted sidewalk when a parallel sidewalk exists on the other side of the roadway.
04 The SIDEWALK CLOSED AHEAD, (ARROW) CROSS HERE (R9-11) sign should be used to indicate to pedestrians that sidewalks beyond the sign are closed and to direct them to open crosswalks, sidewalks, or other travel paths.
05 The SIDEWALK CLOSED, (ARROW) CROSS HERE (R9-11a) sign should be installed just beyond the point to which pedestrians are being redirected.
Support:
06 These signs are typically mounted on a detectable barricade to encourage compliance and to communicate with pedestrians that the sidewalk is closed. Printed signs are not useful to many pedestrians with visual disabilities. A barrier or barricade detectable by a person with a visual disability is sufficient to indicate that a sidewalk is closed. If the barrier is continuous with detectable channelizing devices for an alternate route, accessible signing might not be necessary. An audible information device is needed when the detectable barricade or barrier for an alternate channelized route is not continuous.
Section 6F.15 Special Regulatory Signs
Option:
01 Special regulatory signs may be used based on engineering judgment consistent with regulatory requirements.
Guidance:
02 Special regulatory signs should comply with the general requirements of color, shape, and alphabet size and series. The sign message should be brief, legible, and clear.
Section 6F.16 Warning Sign Function, Design, and Application
Support:
01 TTC zone warning signs (see Figure 6F-4) notify road users of specific situations or conditions on or adjacent to a roadway that might not otherwise be apparent.
Figure 6F-4 Warning Signs and Plaques in Temporary Traffic Control Zones


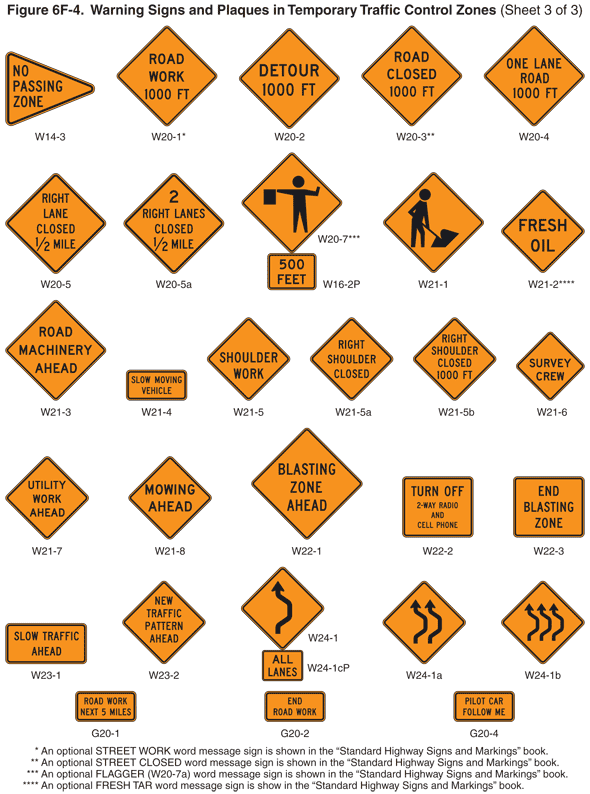
Standard:
02 TTC warning signs shall comply with the Standards for warning signs presented in Part 2 and in FHWA's "Standard Highway Signs and Markings" book (see Section 1A.11). Except as provided in Paragraph 3, TTC warning signs shall be diamond-shaped with a black legend and border on an orange background, except for the W10-1 sign which shall have a black legend and border on a yellow background, and except for signs that are required or recommended in Parts 2 or 7 to have fluorescent yellow-green backgrounds.
Option:
03 Warning signs used for TTC incident management situations may have a black legend and border on a fluorescent pink background.
04 Mounting or space considerations may justify a change from the standard diamond shape.
05 In emergencies, available warning signs having yellow backgrounds may be used if signs with orange or fluorescent pink backgrounds are not at hand.
Guidance:
06 Where roadway or road user conditions require greater emphasis, larger than standard size warning signs should be used, with the symbol or legend enlarged approximately in proportion to the outside dimensions.
07 Where any part of the roadway is obstructed or closed by work activities or incidents, advance warning signs should be installed to alert road users well in advance of these obstructions or restrictions.
08 Where road users include pedestrians, the provision of supplemental audible information or detectable barriers or barricades should be considered for people with visual disabilities.
Support:
09 Detectable barriers or barricades communicate very clearly to pedestrians who have visual disabilities that they can no longer proceed in the direction that they are traveling.
Option:
10 Advance warning signs may be used singly or in combination.
11 Where distances are not displayed on warning signs as part of the message, a supplemental plaque with the distance legend may be mounted immediately below the sign on the same support.
Section 6F.17 Position of Advance Warning Signs
Guidance:
01 Where highway conditions permit, warning signs should be placed in advance of the TTC zone at varying distances depending on roadway type, condition, and posted speed. Table 6C-1 contains information regarding the spacing of advance warning signs. Where a series of two or more advance warning signs is used, the closest sign to the TTC zone should be placed approximately 100 feet for low-speed urban streets to 1,000 feet or more for freeways and expressways.
02 Where multiple advance warning signs are needed on the approach to a TTC zone, the ROAD WORK AHEAD (W20-1) sign should be the first advance warning sign encountered by road users.
Support:
03 Various conditions, such as limited sight distance or obstructions that might require a driver to reduce speed or stop, might require additional advance warning signs.
Option:
04 As an alternative to a specific distance on advance warning signs, the word AHEAD may be used.
Support:
05 At TTC zones on lightly-traveled roads, all of the advance warning signs prescribed for major construction might not be needed.
Option:
06 Utility work, maintenance, or minor construction can occur within the TTC zone limits of a major construction project, and additional warning signs may be needed.
Guidance:
07 Utility, maintenance, and minor construction signing and TTC should be coordinated with appropriate authorities so that road users are not confused or misled by the additional TTC devices.
Section 6F.18 ROAD (STREET) WORK Sign (W20-1)
Guidance:
01 The ROAD (STREET) WORK (W20-1) sign (see Figure 6F-4), which serves as a general warning of obstructions or restrictions, should be located in advance of the work space or any detour, on the road where the work is taking place.
02 Where traffic can enter a TTC zone from a crossroad or a major (high-volume) driveway, an advance warning sign should be used on the crossroad or major driveway.
Standard:
03 The ROAD (STREET) WORK (W20-1) sign shall have the legend ROAD (STREET) WORK, XX FEET, XX MILES, or AHEAD.
Section 6F.19 DETOUR Sign (W20-2)
Guidance:
01 The DETOUR (W20-2) sign (see Figure 6F-4) should be used in advance of a road user detour over a different roadway or route.
Standard:
02 The DETOUR sign shall have the legend DETOUR, XX FEET, XX MILES, or AHEAD.
Section 6F.20 ROAD (STREET) CLOSED Sign (W20-3)
Guidance:
01 The ROAD (STREET) CLOSED (W20-3) sign (see Figure 6F-4) should be used in advance of the point where a highway is closed to all road users, or to all but local road users.
Standard:
02 The ROAD (STREET) CLOSED sign shall have the legend ROAD (STREET) CLOSED, XX FEET, XX MILES, or AHEAD.
Section 6F.21 ONE LANE ROAD Sign (W20-4)
Standard:
01 The ONE LANE ROAD (W20-4) sign (see Figure 6F-4) shall be used only in advance of that point where motor vehicle traffic in both directions must use a common single lane (see Section 6C.10). It shall have the legend ONE LANE ROAD, XX FEET, XX MILES, or AHEAD.
Section 6F.22 Lane(s) Closed Signs (W20-5, W20-5a)
Standard:
01 The Lane(s) Closed sign (see Figure 6F-4) shall be used in advance of that point where one or more through lanes of a multi-lane roadway are closed.
02 For a single lane closure, the Lane Closed (W20-5) sign (see Figure 6F-4) shall have the legend RIGHT (LEFT) LANE CLOSED, XX FEET, XX MILES, or AHEAD. Where two adjacent lanes are closed, the W20-5a sign (see Figure 6F-4) shall have the legend 2 RIGHT (LEFT) LANES CLOSED, XX FEET, XX MILES, or AHEAD.
Section 6F.23 CENTER LANE CLOSED AHEAD Sign (W9-3)
Guidance:
01 The CENTER LANE CLOSED AHEAD (W9-3) sign (see Figure 6F-4) should be used in advance of that point where work occupies the center lane(s) and approaching motor vehicle traffic is directed to the right or left of the work zone in the center lane.
Section 6F.24 Lane Ends Sign (W4-2)
Option:
01 The Lane Ends (W4-2) symbol sign (see Figure 6F-4) may be used to warn drivers of the reduction in the number of lanes for moving motor vehicle traffic in the direction of travel on a multi-lane roadway.
Section 6F.25 ON RAMP Plaque (W13-4P)
Guidance:
01 When work is being done on a ramp, but the ramp remains open, the ON RAMP (W13-4P) plaque (see Figure 6F-4) should be used to supplement the advance ROAD WORK sign.
Section 6F.26 RAMP NARROWS Sign (W5-4)
Guidance:
01 The RAMP NARROWS (W5-4) sign (see Figure 6F-4) should be used in advance of the point where work on a ramp reduces the normal width of the ramp along a part or all of the ramp.
Section 6F.27 SLOW TRAFFIC AHEAD Sign (W23-1)
Option:
01 The SLOW TRAFFIC AHEAD (W23-1) sign (see Figure 6F-4) may be used on a shadow vehicle, usually mounted on the rear of the most upstream shadow vehicle, along with other appropriate signs for mobile operations to warn of slow moving work vehicles. A ROAD WORK (W20-1) sign may also be used with the SLOW TRAFFIC AHEAD sign.
Section 6F.28 EXIT OPEN and EXIT CLOSED Signs (E5-2, E5-2a)
Option:
01 An EXIT OPEN (E5-2) or EXIT CLOSED (E5-2a) sign (see Figure 6F-5) may be used to supplement other warning signs where work is being conducted in the vicinity of an exit ramp and where the exit maneuver for vehicular traffic using the ramp is different from the normal condition.
Figure 6F-5 Exit Open and Closed and Detour Signs
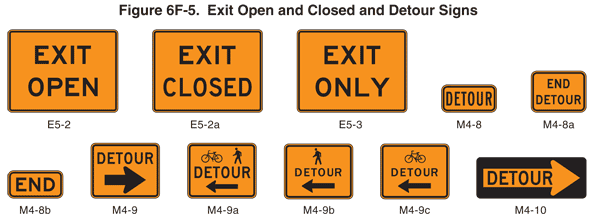
Guidance:
02 When an exit ramp is closed, an EXIT CLOSED sign panel with a black legend and border on an orange background should be placed diagonally across the interchange/intersection guide signs.
Section 6F.29 EXIT ONLY Sign (E5-3)
Option:
01 An EXIT ONLY (E5-3) sign (see Figure 6F-5) may be used to supplement other warning signs where work is being conducted in the vicinity of an exit ramp and where the exit maneuver for vehicular traffic using the ramp is different from the normal condition.
Section 6F.30 NEW TRAFFIC PATTERN AHEAD Sign (W23-2)
Option:
01 A NEW TRAFFIC PATTERN AHEAD (W23-2) sign (see Figure 6F-4) may be used on the approach to an intersection or along a section of roadway to provide advance warning of a change in traffic patterns, such as revised lane usage, roadway geometry, or signal phasing.
Guidance:
02 To retain its effectiveness, the W23-2 sign should be displayed for up to 2 weeks, and then it should be covered or removed until it is needed again.
Section 6F.31 Flagger Signs (W20-7, W20-7a)
Guidance:
01 The Flagger (W20-7) symbol sign (see Figure 6F-4) should be used in advance of any point where a flagger is stationed to control road users.
Option:
02 A distance legend may be displayed on a supplemental plaque below the Flagger sign. The sign may be used with appropriate legends or in conjunction with other warning signs, such as the BE PREPARED TO STOP (W3-4) sign (see Figure 6F-4).
03 The FLAGGER (W20-7a) word message sign with distance legends may be substituted for the Flagger (W20-7) symbol sign.
Section 6F.32 Two-Way Traffic Sign (W6-3)
Guidance:
01 When one roadway of a normally divided highway is closed, with two-way vehicular traffic maintained on the other roadway, the Two-Way Traffic (W6-3) sign (see Figure 6F-4) should be used at the beginning of the two-way vehicular traffic section and at intervals to remind road users of opposing vehicular traffic.
Section 6F.33 Workers Signs (W21-1, W21-1a)
Option:
01 A Workers (W21-1) symbol sign (see Figure 6F-4) may be used to alert road users of workers in or near the roadway.
Guidance:
02 In the absence of other warning devices, a Workers symbol sign should be used when workers are in the roadway.
Option:
03 The WORKERS (W21-1a) word message sign may be used as an alternate to the Workers (W21-1) symbol sign.
Section 6F.34 FRESH OIL (TAR) Sign (W21-2)
Guidance:
01 The FRESH OIL (TAR) (W21-2) sign (see Figure 6F-4) should be used to warn road users of the surface treatment.
Section 6F.35 ROAD MACHINERY AHEAD Sign (W21-3)
Option:
01 The ROAD MACHINERY AHEAD (W21-3) sign (see Figure 6F-4) may be used to warn of machinery operating in or adjacent to the roadway.
Section 6F.36 Motorized Traffic Signs (W8-6, W11-10)
Option:
01 Motorized Traffic (W8-6, W11-10) signs may be used to alert road users to locations where unexpected travel on the roadway or entries into or departures from the roadway by construction vehicles might occur. The TRUCK CROSSING (W8-6) word message sign may be used as an alternate to the Truck Crossing (W11-10) symbol sign (see Figure 6F-4) where there is an established construction vehicle crossing of the roadway.
Support:
02 These locations might be relatively confined or might occur randomly over a segment of roadway.
Section 6F.37 Shoulder Work Signs (W21-5, W21-5a, W21-5b)
Support:
01 Shoulder Work signs (see Figure 6F-4) warn of maintenance, reconstruction, or utility operations on the highway shoulder where the roadway is unobstructed.
Standard:
02 The Shoulder Work sign shall have the legend SHOULDER WORK (W21-5), RIGHT (LEFT) SHOULDER CLOSED (W21-5a), or RIGHT (LEFT) SHOULDER CLOSED XX FT or AHEAD (W21-5b).
Option:
03 The Shoulder Work sign may be used in advance of the point on a non-limited access highway where there is shoulder work. It may be used singly or in combination with a ROAD WORK NEXT XX MILES or ROAD WORK AHEAD sign.
Guidance:
04 On freeways and expressways, the RIGHT (LEFT) SHOULDER CLOSED XX FT or AHEAD (W21-5b) sign followed by RIGHT (LEFT) SHOULDER CLOSED (W21-5a) sign should be used in advance of the point where the shoulder work occurs and should be preceded by a ROAD WORK AHEAD sign.
Section 6F.38 SURVEY CREW Sign (W21-6)
Guidance:
01 The SURVEY CREW (W21-6) sign (see Figure 6F-4) should be used to warn of surveying crews working in or adjacent to the roadway.
Section 6F.39 UTILITY WORK Sign (W21-7)
Option:
01 The UTILITY WORK (W21-7) sign (see Figure 6F-4) may be used as an alternate to the ROAD (STREET) WORK (W20-1) sign for utility operations on or adjacent to a highway.
Support:
02 Typical examples of where the UTILITY WORK sign is used appear in Figures 6H-4, 6H-6, 6H-10, 6H-15, 6H-18, 6H-21, 6H-22, 6H-26, and 6H-33.
Standard:
03 The UTILITY WORK sign shall carry the legend UTILITY WORK, XX FEET, XX MILES, or AHEAD.
Section 6F.40 Signs for Blasting Areas
Support:
01 Radio-Frequency (RF) energy can cause the premature firing of electric detonators (blasting caps) used in TTC zones.
Standard:
02 Road users shall be warned to turn off mobile radio transmitters and cellular telephones where blasting operations occur. A sequence of signs shall be prominently displayed to direct operators of mobile radio equipment, including cellular telephones, to turn off transmitters in a blasting area. These signs shall be covered or removed when there are no explosives in the area or the area is otherwise secured.
Section 6F.41 BLASTING ZONE AHEAD Sign (W22-1)
Standard:
01 The BLASTING ZONE AHEAD (W22-1) sign (see Figure 6F-4) shall be used in advance of any TTC zone where explosives are being used. The TURN OFF 2-WAY RADIO AND CELL PHONE and END BLASTING ZONE signs shall be used in sequence with this sign.
Section 6F.42 TURN OFF 2-WAY RADIO AND CELL PHONE Sign (W22-2)
Standard:
01 The TURN OFF 2-WAY RADIO AND CELL PHONE (W22-2) sign (see Figure 6F-4) shall follow the BLASTING ZONE AHEAD sign and shall be placed at least 1,000 feet before the beginning of the blasting zone.
Section 6F.43 END BLASTING ZONE Sign (W22-3)
Standard:
01 The END BLASTING ZONE (W22-3) sign (see Figure 6F-4) shall be placed a minimum of 1,000 feet past the blasting zone.
Option:
02 The END BLASTING ZONE sign may be placed either with or preceding the END ROAD WORK sign.
Section 6F.44 Shoulder Signs and Plaque (W8-4, W8-9, W8-17, and W8-17P)
Option:
01 The SOFT SHOULDER (W8-4) sign (see Figure 6F-4) may be used to warn of a soft shoulder condition.
02 The LOW SHOULDER (W8-9) sign (see Figure 6F-4) may be used to warn of a shoulder condition where there is an elevation difference of 3 inches or less between the shoulder and the travel lane.
Guidance:
03 The Shoulder Drop Off (W8-17) sign (see Figure 6F-4) should be used when an unprotected shoulder drop-off, adjacent to the travel lane, exceeds 3 inches in depth for a continuous length along the roadway, based on engineering judgment.
Option:
04 A SHOULDER DROP-OFF (W8-17P) supplemental plaque (see Figure 6F-4) may be mounted below the W8-17 sign.
Section 6F.45 UNEVEN LANES Sign (W8-11)
Guidance:
01 The UNEVEN LANES (W8-11) sign (see Figure 6F-4) should be used during operations that create a difference in elevation between adjacent lanes that are open to travel.
Section 6F.46 STEEL PLATE AHEAD Sign (W8-24)
Option:
01 A STEEL PLATE AHEAD (W8-24) sign (see Figure 6F-4) may be used to warn road users that the presence of a temporary steel plate(s) might make the road surface uneven and might create slippery conditions during wet weather.
Section 6F.47 NO CENTER LINE Sign (W8-12)
Guidance:
01 The NO CENTER LINE (W8-12) sign (see Figure 6F-4) should be used when the work obliterates the center line pavement markings. This sign should be placed at the beginning of the TTC zone and repeated at 2-mile intervals in long TTC zones.
Support:
02 Section 6F.78 contains information regarding temporary markings.
Section 6F.48 Reverse Curve Signs (W1-4 Series)
Guidance:
01 In order to give road users advance notice of a lane shift, a Reverse Curve (W1-4, W1-4b, or W1-4c) sign (see Figure 6F-4) should be used when a lane (or lanes) is being shifted to the left or right. If the design speed of the curves is 30 mph or less, a Reverse Turn (W1-3) sign should be used.
Standard:
02 If a Reverse Curve (or Turn) sign is used, the direction of the reverse curve (or turn) shall be appropriately illustrated. Except as provided in Paragraph 3, the number of lanes illustrated on the sign shall be the same as the number of through lanes available to road users.
Option:
03 Where two or more lanes are being shifted, a W1-4 (or W1-3) sign with an ALL LANES (W24-1cP) plaque (see Figure 6F-4) may be used instead of a sign that illustrates the number of lanes.
04 Where more than three lanes are being shifted, the Reverse Curve (or Turn) sign may be rectangular.
Section 6F.49 Double Reverse Curve Signs (W24-1 Series)
Option:
01 The Double Reverse Curve (W24-1, W24-1a, or W24-1b) sign (see Figure 6F-4) may be used where the tangent distance between two reverse curves is less than 600 feet, thus making it difficult for a second Reverse Curve (W1-4 series) sign to be placed between the curves. If the design speed of the curves is 30 mph or less, Double Reverse Turn signs should be used.
Standard:
02 If a Double Reverse Curve (or Turn) sign is used, the direction of the double reverse curve (or turn) shall be appropriately illustrated. Except as provided in Paragraph 3, the number of lanes illustrated on the sign shall be the same as the number of through lanes available to road users.
Option:
03 Where two or more lanes are being shifted, a W24-1 (or Double Reverse Turn sign showing one lane) sign with an ALL LANES (W24-1cP) plaque (see Figure 6F-4) may be used instead of a sign that illustrates the number of lanes.
04 Where more than three lanes are being shifted, the Double Reverse Curve (or Turn) sign may be rectangular.
Section 6F.50 Other Warning Signs
Option:
01 Advance warning signs may be used by themselves or with other advance warning signs.
02 Besides the warning signs specifically related to TTC zones, several other warning signs in Part 2 may apply in TTC zones.
Standard:
03 Except as provided in Section 6F.02, other warning signs that are used in TTC zones shall have black legends and borders on an orange background.
Section 6F.51 Special Warning Signs
Option:
01 Special warning signs may be used based on engineering judgment.
Guidance:
02 Special warning signs should comply with the general requirements of color, shape, and alphabet size and series. The sign message should be brief, legible, and clear.
Section 6F.52 Advisory Speed Plaque (W13-1P)
Option:
01 In combination with a warning sign, an Advisory Speed (W13-1P) plaque (see Figure 6F-4) may be used to indicate a recommended speed through the TTC zone.
Standard:
02 The Advisory Speed plaque shall not be used in conjunction with any sign other than a warning sign, nor shall it be used alone. When used with orange TTC zone signs, this plaque shall have a black legend and border on an orange background. The sign shall be at least 24 x 24 inches in size when used with a sign that is 36 x 36 inches or larger. Except in emergencies, an Advisory Speed plaque shall not be mounted until the recommended speed is determined by the highway agency.
Section 6F.53 Supplementary Distance Plaque (W7-3aP)
Option:
01 In combination with a warning sign, a Supplementary Distance (W7-3aP) plaque (see Figure 6F-4) with the legend NEXT XX MILES may be used to indicate the length of highway over which a work activity is being conducted, or over which a condition exists in the TTC zone.
02 In long TTC zones, Supplementary Distance plaques with the legend NEXT XX MILES may be placed in combination with warning signs at regular intervals within the zone to indicate the remaining length of highway over which the TTC work activity or condition exists.
Standard:
03 The Supplementary Distance plaque with the legend NEXT XX MILES shall not be used in conjunction with any sign other than a warning sign, nor shall it be used alone. When used with orange TTC zone signs, this plaque shall have a black legend and border on an orange background. The sign shall be at least 30 x 24 inches in size when used with a sign that is 36 x 36 inches or larger.
Guidance:
04 When used in TTC zones, the Supplementary Distance plaque with the legend NEXT XX MILES should be placed below the initial warning sign designating that, within the approaching zone, a temporary work activity or condition exists.
Section 6F.54 Motorcycle Plaque (W8-15P)
Option:
01 A Motorcycle (W8-15P) plaque (see Figure 6F-4) may be mounted below a LOOSE GRAVEL (W8-7) sign, a GROOVED PAVEMENT (W8-15) sign, a METAL BRIDGE DECK (W8-16) sign, or a STEEL PLATE AHEAD (W8-24) sign if the warning is intended to be directed primarily to motorcyclists.
Section 6F.55 Guide Signs
Support:
01 Guide signs along highways provide road users with information to help them along their way through the TTC zone. The design of guide signs is presented in Part 2.
Guidance:
02 The following guide signs should be used in TTC zones as needed:
- Standard route markings, where temporary route changes are necessary,
- Directional signs and street name signs, and
- Special guide signs relating to the condition or work being done.
Standard:
03 If additional temporary guide signs are used in TTC zones, they shall have a black legend and border on an orange background.
Option:
04 Guide signs used in TTC incident management situations may have a black legend and border on a fluorescent pink background.
05 When directional signs and street name signs are used in conjunction with detour routing, these signs may have a black legend and border on an orange background.
06 When permanent directional signs or permanent street name signs are used in conjunction with detour signing, they may have a white legend on a green background.
Section 6F.56 ROAD WORK NEXT XX MILES Sign (G20-1)
Guidance:
01 The ROAD WORK NEXT XX MILES (G20-1) sign (see Figure 6F-4) should be installed in advance of TTC zones that are more than 2 miles in length.
Option:
02 The ROAD WORK NEXT XX MILES sign may be mounted on a Type 3 Barricade. The sign may also be used for TTC zones of shorter length.
Standard:
03 The distance displayed on the ROAD WORK NEXT XX MILES sign shall be stated to the nearest whole mile.
Section 6F.57 END ROAD WORK Sign (G20-2)
Guidance:
01 When used, the END ROAD WORK (G20-2) sign (see Figure 6F-4) should be placed near the downstream end of the termination area, as determined by engineering judgment.
Option:
02 The END ROAD WORK sign may be installed on the back of a warning sign facing the opposite direction of road users or on the back of a Type 3 Barricade.
Section 6F.58 PILOT CAR FOLLOW ME Sign (G20-4)
Standard:
01 The PILOT CAR FOLLOW ME (G20-4) sign (see Figure 6F-4) shall be mounted in a conspicuous position on the rear of a vehicle used for guiding one-way vehicular traffic through or around a TTC zone (see Section 6C.13).
Section 6F.59 Detour Signs (M4-8, M4-8a, M4-8b, M4-9, M4-9a, M4-9b, M4-9c, and M4-10)
Standard:
01 Each detour shall be adequately marked with standard temporary route signs and destination signs.
Option:
02 Detour signs in TTC incident management situations may have a black legend and border on a fluorescent pink background.
03 The Detour Arrow (M4-10) sign (see Figure 6F-5) may be used where a detour route has been established.
04 The DETOUR (M4-8) sign (see Figure 6F-5) may be mounted at the top of a route sign assembly to mark a temporary route that detours from a highway, bypasses a section closed by a TTC zone, and rejoins the highway beyond the TTC zone.
Guidance:
05 The Detour Arrow (M4-10) sign should normally be mounted just below the ROAD CLOSED (R11-2, R11-3a, or R11-4) sign. The Detour Arrow sign should include a horizontal arrow pointed to the right or left as required.
06 The DETOUR (M4-9) sign (see Figure 6F-5) should be used for unnumbered highways, for emergency situations, for periods of short durations, or where, over relatively short distances, road users are guided along the detour and back to the desired highway without route signs.
07 A Street Name sign should be placed above, or the street name should be incorporated into, a DETOUR (M4-9) sign to indicate the name of the street being detoured.
Option:
08 The END DETOUR (M4-8a) or END (M4-8b) sign (see Figure 6F-5) may be used to indicate that the detour has ended.
Guidance:
09 When the END DETOUR sign is used on a numbered highway, the sign should be mounted above a route sign after the downstream end of the detour.
10 The Pedestrian/Bicycle Detour (M4-9a) sign (see Figure 6F-5) should be used where a pedestrian/bicycle detour route has been established because of the closing of a pedestrian/bicycle facility to through traffic.
Standard:
11 If used, the Pedestrian/Bicycle Detour sign shall have an arrow pointing in the appropriate direction.
Option:
12 The arrow on a Pedestrian/Bicycle Detour sign may be on the sign face or on a supplemental plaque.
13 The Pedestrian Detour (M4-9b) sign or Bicycle Detour (M4-9c) sign (see Figure 6F-5) may be used where a pedestrian or bicycle detour route (not both) has been established because of the closing of the pedestrian or bicycle facility to through traffic.
Section 6F.60 Portable Changeable Message Signs
Support:
01 Portable changeable message signs (PCMS) are TTC devices installed for temporary use with the flexibility to display a variety of messages. In most cases, portable changeable message signs follow the same provisions for design and application as those given for changeable message signs in Chapter 2L. The information in this Section describes situations where the provisions for portable changeable message signs differ from those given in Chapter 2L.
02 Portable changeable message signs are used most frequently on high-density urban freeways, but have applications on all types of highways where highway alignment, road user routing problems, or other pertinent conditions require advance warning and information.
03 Portable changeable message signs have a wide variety of applications in TTC zones including: roadway, lane, or ramp closures; incident management; width restriction information; speed control or reductions; advisories on work scheduling; road user management and diversion; warning of adverse conditions or special events; and other operational control.
04 The primary purpose of portable changeable message signs in TTC zones is to advise the road user of unexpected situations. Portable changeable message signs are particularly useful as they are capable of:
- Conveying complex messages,
- Displaying real time information about conditions ahead, and
- Providing information to assist road users in making decisions prior to the point where actions must be taken.
05 Some typical applications include the following:
- Where the speed of vehicular traffic is expected to drop substantially;
- Where significant queuing and delays are expected;
- Where adverse environmental conditions are present;
- Where there are changes in alignment or surface conditions;
- Where advance notice of ramp, lane, or roadway closures is needed;
- Where crash or incident management is needed; and/or
- Where changes in the road user pattern occur.
Guidance:
06 The components of a portable changeable message sign should include: a message sign, control systems, a power source, and mounting and transporting equipment. The front face of the sign should be covered with a protective material.
Standard:
07 Portable changeable message signs shall comply with the applicable design and application principles established in Chapter 2A. Portable changeable message signs shall display only traffic operational, regulatory, warning, and guidance information, and shall not be used for advertising messages.
Support:
08 Section 2L.02 contains information regarding overly simplistic or vague messages that is also applicable to portable changeable message signs.
Standard:
09 The colors used for legends on portable changeable message signs shall comply with those shown in Table 2A-5.
Support:
10 Section 2L.04 contains information regarding the luminance, luminance contrast, and contrast orientation that is also applicable to portable changeable message signs.
Guidance:
11 Portable changeable message signs should be visible from 1/2 mile under both day and night conditions.
Support:
12 Section 2B.13 contains information regarding the design of portable changeable message signs that are used to display speed limits that change based on operational conditions, or are used to display the speed at which approaching drivers are traveling.
Guidance:
13 A portable changeable message sign should be limited to three lines of eight characters per line or should consist of a full matrix display.
14 Except as provided in Paragraph 15, the letter height used for portable changeable message sign messages should be a minimum of 18 inches.
Option:
15 For portable changeable message signs mounted on service patrol trucks or other incident response vehicles, a letter height as short as 10 inches may be used. Shorter letter sizes may also be used on a portable changeable message sign used on low speed facilities provided that the message is legible from at least 650 feet.
16 The portable changeable message sign may vary in size.
Guidance:
17 Messages on a portable changeable message sign should consist of no more than two phases, and a phase should consist of no more than three lines of text. Each phase should be capable of being understood by itself, regardless of the order in which it is read. Messages should be centered within each line of legend. If more than one portable changeable message sign is simultaneously legible to road users, then only one of the signs should display a sequential message at any given time.
Support:
18 Road users have difficulties in reading messages displayed in more than two phases on a typical three-line portable changeable message sign.
Standard:
19 Techniques of message display such as animation, rapid flashing, dissolving, exploding, scrolling, travelling horizontally or vertically across the face of the sign, or other dynamic elements shall not be used.
Guidance:
20 When a message is divided into two phases, the display time for each phase should be at least 2 seconds, and the sum of the display times for both of the phases should be a maximum of 8 seconds.
21 All messages should be designed with consideration given to the principles provided in this Section and also taking into account the following:
- The message should be as brief as possible and should contain three thoughts (with each thought preferably shown on its own line) that convey:
- The problem or situation that the road user will encounter ahead,
- The location of or distance to the problem or situation, and
- The recommended driver action.
- If more than two phases are needed to display a message, additional portable changeable message signs should be used. When multiple portable changeable message signs are needed, they should be placed on the same side of the roadway and they should be separated from each other by a distance of at least 1,000 feet on freeways and expressways, and by a distance of at least 500 feet on other types of highways.
Standard:
22 When the word messages shown in Tables 1A-1 or 1A-2 need to be abbreviated on a portable changeable message sign, the provisions described in Section 1A.15 shall be followed.
23 In order to maintain legibility, portable changeable message signs shall automatically adjust their brightness under varying light conditions.
24 The control system shall include a display screen upon which messages can be reviewed before being displayed on the message sign. The control system shall be capable of maintaining memory when power is unavailable.
25 Portable changeable message signs shall be equipped with a power source and a battery back-up to provide continuous operation when failure of the primary power source occurs.
26 The mounting of portable changeable message signs on a trailer, a large truck, or a service patrol truck shall be such that the bottom of the message sign shall be a minimum of 7 feet above the roadway in urban areas and 5 feet above the roadway in rural areas when it is in the operating mode.
Guidance:
27 Portable changeable message signs should be used as a supplement to and not as a substitute for conventional signs and pavement markings.
28 When portable changeable message signs are used for route diversion, they should be placed far enough in advance of the diversion to allow road users ample opportunity to perform necessary lane changes, to adjust their speed, or to exit the affected highway.
29 Portable changeable message signs should be sited and aligned to provide maximum legibility and to allow time for road users to respond appropriately to the portable changeable message sign message.
30 Portable changeable message signs should be placed off the shoulder of the roadway and behind a traffic barrier, if practical. Where a traffic barrier is not available to shield the portable changeable message sign, it should be placed off the shoulder and outside of the clear zone. If a portable changeable message sign has to be placed on the shoulder of the roadway or within the clear zone, it should be delineated with retroreflective TTC devices.
31 When portable changeable message signs are used in TTC zones, they should display only TTC messages.
32 When portable changeable message signs are not being used to display TTC messages, they should be relocated such that they are outside of the clear zone or shielded behind a traffic barrier and turned away from traffic. If relocation or shielding is not practical, they should be delineated with retroreflective TTC devices.
33 Portable changeable message sign trailers should be delineated on a permanent basis by affixing retroreflective material, known as conspicuity material, in a continuous line on the face of the trailer as seen by oncoming road users.
Section 6F.61 Arrow Boards
Standard:
01 An arrow board shall be a sign with a matrix of elements capable of either flashing or sequential displays. This sign shall provide additional warning and directional information to assist in merging and controlling road users through or around a TTC zone.
Guidance:
02 An arrow board in the arrow or chevron mode should be used to advise approaching traffic of a lane closure along major multi-lane roadways in situations involving heavy traffic volumes, high speeds, and/or limited sight distances, or at other locations and under other conditions where road users are less likely to expect such lane closures.
03 If used, an arrow board should be used in combination with appropriate signs, channelizing devices, or other TTC devices.
04 An arrow board should be placed on the shoulder of the roadway or, if practical, farther from the traveled lane. It should be delineated with retroreflective TTC devices. When an arrow board is not being used, it should be removed; if not removed, it should be shielded; or if the previous two options are not feasible, it should be delineated with retroreflective TTC devices.
Standard:
05 Arrow boards shall meet the minimum size, legibility distance, number of elements, and other specifications shown in Figure 6F-6.
Figure 6F-6 Advance Warning Arrow Board Display Specifications
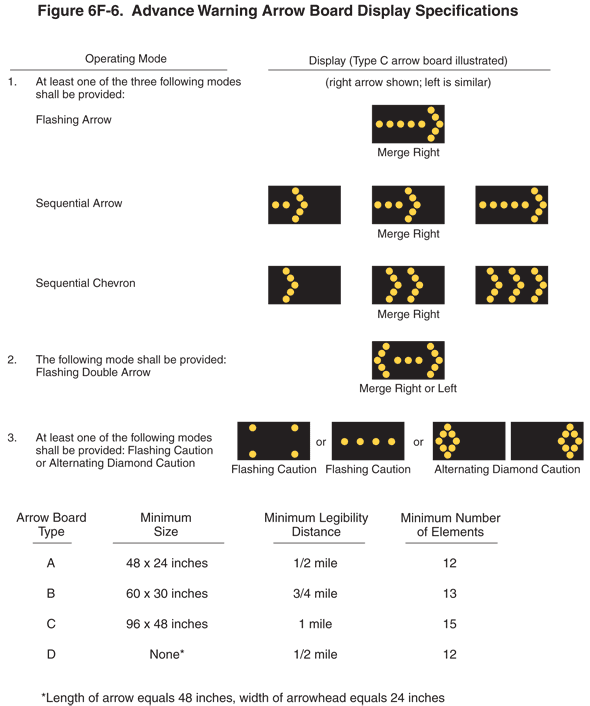
Support:
06 Type A arrow boards are appropriate for use on low-speed urban streets. Type B arrow boards are appropriate for intermediate-speed facilities and for maintenance or mobile operations on high-speed roadways. Type C arrow boards are intended to be used on high-speed, high-volume motor vehicle traffic control projects. Type D arrow boards are intended for use on vehicles authorized by the State or local agency.
Standard:
07 Type A, B, and C arrow boards shall have solid rectangular appearances. A Type D arrow board shall conform to the shape of the arrow.
08 All arrow boards shall be finished in non-reflective black. The arrow board shall be mounted on a vehicle, a trailer, or other suitable support.
Guidance:
09 The minimum mounting height, measured vertically from the bottom of the board to the roadway below it or to the elevation of the near edge of the roadway, of an arrow board should be 7 feet , except on vehicle-mounted arrow boards, which should be as high as practical.
10 A vehicle-mounted arrow board should be provided with remote controls.
Standard:
11 Arrow board elements shall be capable of at least a 50 percent dimming from full brilliance. The dimmed mode shall be used for nighttime operation of arrow boards.
Guidance:
12 Full brilliance should be used for daytime operation of arrow boards.
Standard:
13 The arrow board shall have suitable elements capable of the various operating modes. The color presented by the elements shall be yellow.
Guidance:
14 If an arrow board consisting of a bulb matrix is used, the elements should be recess-mounted or equipped with an upper hood of not less than 180 degrees.
Standard:
15 The minimum element on-time shall be 50 percent for the flashing mode, with equal intervals of 25 percent for each sequential phase. The flashing rate shall be not less than 25 or more than 40 flashes per minute.
16 An arrow board shall have the following three mode selections:
- A Flashing Arrow, Sequential Arrow, or Sequential Chevron mode;
- A flashing Double Arrow mode; and
- A flashing Caution or Alternating Diamond mode.
17 An arrow board in the arrow or chevron mode shall be used only for stationary or moving lane closures on multi-lane roadways.
18 For shoulder work, blocking the shoulder, for roadside work near the shoulder, or for temporarily closing one lane on a two-lane, two-way roadway, an arrow board shall be used only in the caution mode.
Guidance:
19 For a stationary lane closure, the arrow board should be located on the shoulder at the beginning of the merging taper.
20 Where the shoulder is narrow, the arrow board should be located in the closed lane.
Standard:
21 When arrow boards are used to close multiple lanes, a separate arrow board shall be used for each closed lane.
Guidance:
22 When arrow boards are used to close multiple lanes, if the first arrow board is placed on the shoulder, the second arrow board should be placed in the first closed lane at the upstream end of the second merging taper (see Figure 6H-37). When the first arrow board is placed in the first closed lane, the second arrow board should be placed in the second closed lane at the downstream end of the second merging taper.
23 For mobile operations where a lane is closed, the arrow board should be located to provide adequate separation from the work operation to allow for appropriate reaction by approaching drivers.
Standard:
24 A vehicle displaying an arrow board shall be equipped with high-intensity rotating, flashing, oscillating, or strobe lights.
25 Arrow boards shall only be used to indicate a lane closure. Arrow boards shall not be used to indicate a lane shift.
Option:
26 A portable changeable message sign may be used to simulate an arrow board display.
Section 6F.62 High-Level Warning Devices (Flag Trees)
Option:
01 A high-level warning device (flag tree) may supplement other TTC devices in TTC zones.
Support:
02 A high-level warning device is designed to be seen over the top of typical passenger cars. A typical high-level warning device is shown in Figure 6F-2.
Standard:
03 A high-level warning device shall consist of a minimum of two flags with or without a Type B high-intensity flashing warning light. The distance from the roadway to the bottom of the lens of the light and to the lowest point of the flag material shall be not less than 8 feet. The flag shall be 16 inches square or larger and shall be orange or fluorescent red-orange in color.
Option:
04 An appropriate warning sign may be mounted below the flags.
Support:
05 High-level warning devices are most commonly used in high-density road user situations to warn road users of short-term operations.
Section 6F.63 Channelizing Devices
Standard:
01 Designs of various channelizing devices shall be as shown in Figure 6F–7. All channelizing devices shall be crashworthy.
Figure 6F-7 Channelizing Devices
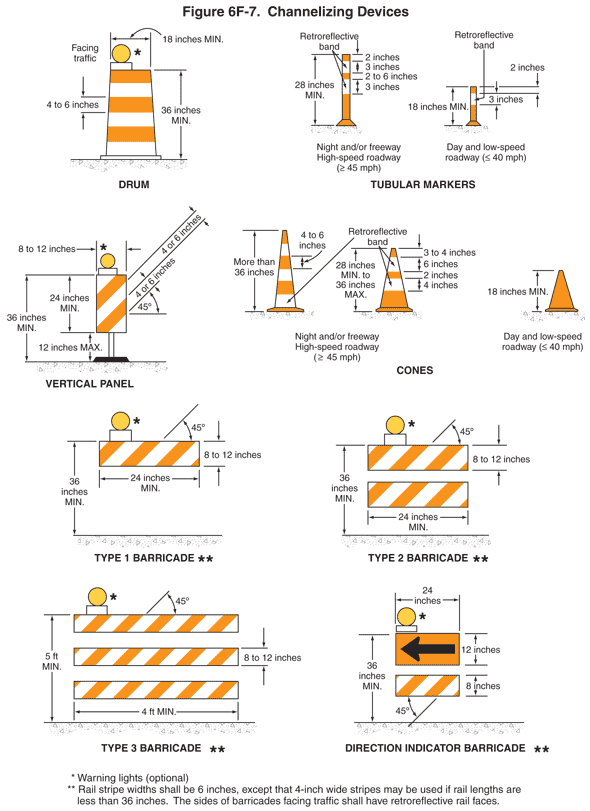
Support:
02 The function of channelizing devices is to warn road users of conditions created by work activities in or near the roadway and to guide road users. Channelizing devices include cones, tubular markers, vertical panels, drums, barricades, and longitudinal channelizing devices.
03 Channelizing devices provide for smooth and gradual vehicular traffic flow from one lane to another, onto a bypass or detour, or into a narrower traveled way. They are also used to channelize vehicular traffic away from the work space, pavement drop-offs, pedestrian or shared-use paths, or opposing directions of vehicular traffic.
Standard:
04 Devices used to channelize pedestrians shall be detectable to users of long canes and visible to persons having low vision.
05 Where channelizing devices are used to channelize pedestrians, there shall be continuous detectable bottom and top surfaces to be detectable to users of long canes. The bottom of the bottom surface shall be no higher than 2 inches above the ground. The top of the top surface shall be no lower than 32 inches above the ground.
Option:
06 A gap not exceeding 2 inches between the bottom rail and the ground surface may be used to facilitate drainage.
Guidance:
07 Where multiple channelizing devices are aligned to form a continuous pedestrian channelizer, connection points should be smooth to optimize long-cane and hand trailing.
08 The spacing between cones, tubular markers, vertical panels, drums, and barricades should not exceed a distance in feet equal to 1.0 times the speed limit in mph when used for taper channelization, and a distance in feet equal to 2.0 times the speed limit in mph when used for tangent channelization.
09 When channelizing devices have the potential of leading vehicular traffic out of the intended vehicular traffic space as shown in Figure 6H-39, the channelizing devices should be extended a distance in feet of 2.0 times the speed limit in mph beyond the downstream end of the transition area.
Option:
10 Warning lights (see Section 6F.83) may be added to channelizing devices in areas with frequent fog, snow, or severe roadway curvature, or where visual distractions are present.
Standard:
11 Warning lights shall flash when placed on channelizing devices used alone or in a cluster to warn of a condition. Except for the sequential flashing warning lights discussed in Paragraphs 12 and 13, warning lights placed on channelizing devices used in a series to channelize road users shall be steady-burn.
Option:
12 A series of sequential flashing warning lights may be placed on channelizing devices that form a merging taper in order to increase driver detection and recognition of the merging taper.
Standard:
13 When used, the successive flashing of the sequential warning lights shall occur from the upstream end of the merging taper to the downstream end of the merging taper in order to identify the desired vehicle path. Each warning light in the sequence shall be flashed at a rate of not less than 55 nor more than 75 times per minute.
14 The retroreflective material used on channelizing devices shall have a smooth, sealed outer surface that will display a similar color day or night.
Option:
15 The name and telephone number of the highway agency, contractor, or supplier may be displayed on the non-retroreflective surface of all types of channelizing devices.
Standard:
16 The letters and numbers of the name and telephone number shall be non-retroreflective and not over 2 inches in height.
Guidance:
17 Particular attention should be given to maintaining the channelizing devices to keep them clean, visible, and properly positioned at all times.
Standard:
18 Devices that are damaged or have lost a significant amount of their retroreflectivity and effectiveness shall be replaced.
Section 6F.64 Cones
Standard:
01 Cones (see Figure 6F-7) shall be predominantly orange and shall be made of a material that can be struck without causing damage to the impacting vehicle. For daytime and low-speed roadways, cones shall be not less than 18 inches in height. When cones are used on freeways and other high-speed highways or at night on all highways, or when more conspicuous guidance is needed, cones shall be a minimum of 28 inches in height.
02 For nighttime use, cones shall be retroreflectorized or equipped with lighting devices for maximum visibility. Retroreflectorization of cones that are 28 to 36 inches in height shall be provided by a 6-inch wide white band located 3 to 4 inches from the top of the cone and an additional 4-inch wide white band located approximately 2 inches below the 6-inch band.
03 Retroreflectorization of cones that are more than 36 inches in height shall be provided by horizontal, circumferential, alternating orange and white retroreflective stripes that are 4 to 6 inches wide. Each cone shall have a minimum of two orange and two white stripes with the top stripe being orange. Any non-retroreflective spaces between the orange and white stripes shall not exceed 3 inches in width.
Option:
04 Traffic cones may be used to channelize road users, divide opposing vehicular traffic lanes, divide lanes when two or more lanes are kept open in the same direction, and delineate short duration maintenance and utility work.
Guidance:
05 Steps should be taken to minimize the possibility of cones being blown over or displaced by wind or moving vehicular traffic.
Option:
06 Cones may be doubled up to increase their weight.
Support:
07 Some cones are constructed with bases that can be filled with ballast. Others have specially weighted bases, or weight such as sandbag rings that can be dropped over the cones and onto the base to provide added stability.
Guidance:
08 Ballast should be kept to the minimum amount needed.
Section 6F.65 Tubular Markers
Standard:
01 Tubular markers (see Figure 6F-7) shall be predominantly orange and shall be not less than 18 inches high and 2 inches wide facing road users. They shall be made of a material that can be struck without causing damage to the impacting vehicle.
02 Tubular markers shall be a minimum of 28 inches in height when they are used on freeways and other high-speed highways, on all highways during nighttime, or whenever more conspicuous guidance is needed.
03 For nighttime use, tubular markers shall be retroreflectorized. Retroreflectorization of tubular markers that have a height of less than 42 inches shall be provided by two 3-inch wide white bands placed a maximum of 2 inches from the top with a maximum of 6 inches between the bands. Retroreflectorization of tubular markers that have a height of 42 inches or more shall be provided by four 4- to 6-inch wide alternating orange and white stripes with the top stripe being orange.
Guidance:
04 Tubular markers have less visible area than other devices and should be used only where space restrictions do not allow for the use of other more visible devices.
05 Tubular markers should be stabilized by affixing them to the pavement, by using weighted bases, or weights such as sandbag rings that can be dropped over the tubular markers and onto the base to provide added stability. Ballast should be kept to the minimum amount needed.
Option:
06 Tubular markers may be used effectively to divide opposing lanes of road users, divide vehicular traffic lanes when two or more lanes of moving vehicular traffic are kept open in the same direction, and to delineate the edge of a pavement drop off where space limitations do not allow the use of larger devices.
Standard:
07 A tubular marker shall be attached to the pavement to display the minimum 2-inch width to the approaching road users.
Section 6F.66 Vertical Panels
Standard:
01 Vertical panels (see Figure 6F-7) shall have retroreflective striped material that is 8 to 12 inches in width and at least 24 inches in height. They shall have alternating diagonal orange and white retroreflective stripes sloping downward at an angle of 45 degrees in the direction vehicular traffic is to pass.
02 Where the height of the retroreflective material on the vertical panel is 36 inches or more, a stripe width of 6 inches shall be used.
Option:
03 Where the height of the retroreflective material on the vertical panel is less than 36 inches, a stripe width of 4 inches may be used.
04 Where space is limited, vertical panels may be used to channelize vehicular traffic, divide opposing lanes, or replace barricades.
Section 6F.67 Drums
Standard:
01 Drums (see Figure 6F-7) used for road user warning or channelization shall be constructed of lightweight, deformable materials. They shall be a minimum of 36 inches in height and have at least an 18-inch minimum width regardless of orientation. Metal drums shall not be used. The markings on drums shall be horizontal, circumferential, alternating orange and white retroreflective stripes 4 to 6 inches wide. Each drum shall have a minimum of two orange and two white stripes with the top stripe being orange. Any non-retroreflectorized spaces between the horizontal orange and white stripes shall not exceed 3 inches wide. Drums shall have closed tops that will not allow collection of construction debris or other debris.
Support:
02 Drums are highly visible, have good target value, give the appearance of being formidable obstacles and, therefore, command the respect of road users. They are portable enough to be shifted from place to place within a TTC zone in order to accommodate changing conditions, but are generally used in situations where they will remain in place for a prolonged period of time.
Option:
03 Although drums are most commonly used to channelize or delineate road user flow, they may also be used alone or in groups to mark specific locations.
Guidance:
04 Drums should not be weighted with sand, water, or any material to the extent that would make them hazardous to road users or workers when struck. Drums used in regions susceptible to freezing should have drain holes in the bottom so that water will not accumulate and freeze causing a hazard if struck by a road user.
Standard:
05 Ballast shall not be placed on the top of a drum.
Section 6F.68 Type 1, 2, or 3 Barricades
Support:
01 A barricade is a portable or fixed device having from one to three rails with appropriate markings and is used to control road users by closing, restricting, or delineating all or a portion of the right-of-way.
02 As shown in Figure 6F-7, barricades are classified as Type 1, Type 2, or Type 3.
Standard:
03 Stripes on barricade rails shall be alternating orange and white retroreflective stripes sloping downward at an angle of 45 degrees in the direction road users are to pass. Except as provided in Paragraph 4, the stripes shall be 6 inches wide.
Option:
04 When rail lengths are less than 36 inches, 4-inch wide stripes may be used.
Standard:
05 The minimum length for Type 1 and Type 2 Barricades shall be 24 inches, and the minimum length for Type 3 Barricades shall be 48 inches. Each barricade rail shall be 8 to 12 inches wide. Barricades used on freeways, expressways, and other high-speed roadways shall have a minimum of 270 square inches of retroreflective area facing road users.
Guidance:
06 Where barricades extend entirely across a roadway, the stripes should slope downward in the direction toward which road users must turn.
07 Where both right and left turns are provided, the barricade stripes should slope downward in both directions from the center of the barricade or barricades.
08 Where no turns are intended, the stripes should be positioned to slope downward toward the center of the barricade or barricades.
09 Barricade rails should be supported in a manner that will allow them to be seen by the road user, and in a manner that provides a stable support that is not easily blown over or displaced.
10 The width of the existing pedestrian facility should be provided for the temporary facility if practical. Traffic control devices and other construction materials and features should not intrude into the usable width of the sidewalk, temporary pathway, or other pedestrian facility. When it is not possible to maintain a minimum width of 60 inches throughout the entire length of the pedestrian pathway, a 60 x 60-inch passing space should be provided at least every 200 feet to allow individuals in wheelchairs to pass.
11 Barricade rail supports should not project into pedestrian circulation routes more than 4 inches from the support between 27 and 80 inches from the surface as described in Section 4.4.1 of the "Americans with Disabilities Act Accessibility Guidelines for Buildings and Facilities (ADAAG)" (see Section 1A.11).
Option:
12 For Type 1 Barricades, the support may include other unstriped horizontal rails necessary to provide stability.
Guidance:
13 On high-speed expressways or in other situations where barricades may be susceptible to overturning in the wind, ballasting should be used.
Option:
14 Sandbags may be placed on the lower parts of the frame or the stays of barricades to provide the required ballast.
Support:
15 Type 1 or Type 2 Barricades are intended for use in situations where road user flow is maintained through the TTC zone.
Option:
16 Barricades may be used alone or in groups to mark a specific condition or they may be used in a series for channelizing road users.
17 Type 1 Barricades may be used on conventional roads or urban streets.
Guidance:
18 Type 2 or Type 3 Barricades should be used on freeways and expressways or other high-speed roadways. Type 3 Barricades should be used to close or partially close a road.
Option:
19 Type 3 Barricades used at a road closure may be placed completely across a roadway or from curb to curb.
Guidance:
20 Where provision is made for access of authorized equipment and vehicles, the responsibility for Type 3 Barricades should be assigned to a person who will provide proper closure at the end of each work day.
Support:
21 When a highway is legally closed but access must still be allowed for local road users, barricades usually are not extended completely across the roadway.
Standard:
22 A sign shall be installed with the appropriate legend concerning permissible use by local road users (see Section 6F.09). Adequate visibility of the barricades from both directions shall be provided.
Option:
23 Signs may be installed on barricades (see Section 6F.03).
Section 6F.69 Direction Indicator Barricades
Standard:
01 The Direction Indicator Barricade (see Figure 6F-7) shall consist of a One-Direction Large Arrow (W1-6) sign mounted above a diagonal striped, horizontally aligned, retroreflective rail.
02 The One-Direction Large Arrow (W1-6) sign shall be black on an orange background. The stripes on the bottom rail shall be alternating orange and white retroreflective stripes sloping downward at an angle of 45 degrees in the direction road users are to pass. The stripes shall be 4 inches wide. The One-Direction Large Arrow (W1-6) sign shall be 24 x 12 inches. The bottom rail shall have a length of 24 inches and a height of 8 inches.
Option:
03 The Direction Indicator Barricade may be used in tapers, transitions, and other areas where specific directional guidance to drivers is necessary.
Guidance:
04 If used, Direction Indicator Barricades should be used in series to direct the driver through the transition and into the intended travel lane.
Section 6F.70 Temporary Traffic Barriers as Channelizing Devices
Support:
01 Temporary traffic barriers are not TTC devices in themselves; however, when placed in a position identical to a line of channelizing devices and marked and/or equipped with appropriate channelization features to provide guidance and warning both day and night, they serve as TTC devices.
Standard:
02 Temporary traffic barriers serving as TTC devices shall comply with requirements for such devices as set forth throughout Part 6.
03 Temporary traffic barriers (see Section 6F.85) shall not be used solely to channelize road users, but also to protect the work space. If used to channelize vehicular traffic, the temporary traffic barrier shall be supplemented with delineation, pavement markings, or channelizing devices for improved daytime and nighttime visibility.
Guidance:
04 Temporary traffic barriers should not be used for a merging taper except in low-speed urban areas.
05 When it is necessary to use a temporary traffic barrier for a merging taper in low-speed urban areas or for a constricted/restricted TTC zone, the taper length should be designed to optimize road user operations considering the available geometric conditions.
Standard:
06 When it is necessary to use a temporary traffic barrier for a merging taper in low-speed urban areas or for a constricted/restricted TTC zone, the taper shall be delineated.
Guidance:
07 When used for channelization, temporary traffic barriers should be of a light color for increased visibility.
Section 6F.71 Longitudinal Channelizing Devices
Support:
01 Longitudinal channelizing devices are lightweight, deformable devices that are highly visible, have good target value, and can be connected together.
Standard:
02 If used singly as Type 1, 2, or 3 barricades, longitudinal channelizing devices shall comply with the general size, color, stripe pattern, retroreflectivity, and placement characteristics established for the devices described in this Chapter.
Guidance:
03 If used to channelize vehicular traffic at night, longitudinal channelizing devices should be supplemented with retroreflective material or delineation for improved nighttime visibility.
Option:
04 Longitudinal channelizing devices may be used instead of a line of cones, drums, or barricades.
05 Longitudinal channelizing devices may be hollow and filled with water as a ballast.
06 Longitudinal channelizing devices may be used for pedestrian traffic control.
Standard:
07 If used for pedestrian traffic control, longitudinal channelizing devices shall be interlocked to delineate or channelize flow. The interlocking devices shall not have gaps that allow pedestrians to stray from the channelizing path.
Guidance:
08 Longitudinal channelizing devices have not met the crashworthy requirements for temporary traffic barriers and should not be used to shield obstacles or provide positive protection for pedestrians or workers.
Section 6F.72 Temporary Lane Separators
Option:
01 Temporary lane separators may be used to channelize road users, to divide opposing vehicular traffic lanes, to divide lanes when two or more lanes are open in the same direction, and to provide continuous pedestrian channelization.
Standard:
02 Temporary lane separators shall be crashworthy. Temporary lane separators shall have a maximum height of 4 inches and a maximum width of 1 foot, and shall have sloping sides in order to facilitate crossover by emergency vehicles.
Option:
03 Temporary lane separators may be supplemented with any of the approved channelizing devices contained in this Chapter, such as tubular markers, vertical panels, and opposing traffic lane dividers.
Standard:
04 If appropriate channelizing devices are used to supplement a temporary lane separator, the channelizing devices shall be retroreflectorized to provide nighttime visibility. If channelizing devices are not used, the temporary lane separator shall contain retroreflectorization to enhance its visibility.
Guidance:
05 A temporary lane separator should be stabilized by affixing it to the pavement in a manner suitable to its design, while allowing the unit to be shifted from place to place within the TTC zone in order to accommodate changing conditions.
Standard:
06 At pedestrian crossing locations, temporary lane separators shall have an opening or be shortened to provide a pathway that is at least 60 inches wide for crossing pedestrians.
Section 6F.73 Other Channelizing Devices
Option:
01 Channelizing devices other than those described in this Chapter may be used in special situations based on an engineering study.
Guidance:
02 Other channelizing devices should comply with the general size, color, stripe pattern, retroreflection, and placement characteristics established for the devices described in this Chapter.
Section 6F.74 Detectable Edging for Pedestrians
Support:
01 Individual channelizing devices, tape or rope used to connect individual devices, other discontinuous barriers and devices, and pavement markings are not detectable by persons with visual disabilities and are incapable of providing detectable path guidance on temporary or realigned sidewalks or other pedestrian facilities.
Guidance:
02 When it is determined that a facility should be accessible to and detectable by pedestrians with visual disabilities, a continuously detectable edging should be provided throughout the length of the facility such that it can be followed by pedestrians using long canes for guidance. This edging should protrude at least 6 inches above the surface of the sidewalk or pathway, with the bottom of the edging a maximum of 2.5 inches above the surface. This edging should be continuous throughout the length of the facility except for gaps at locations where pedestrians or vehicles will be turning or crossing. This edging should consist of a prefabricated or formed-in-place curbing or other continuous device that is placed along the edge of the sidewalk or walkway. This edging should be firmly attached to the ground or to other devices. Adjacent sections of this edging should be interconnected such that the edging is not displaced by pedestrian or vehicular traffic or work operations, and such that it does not constitute a hazard to pedestrians, workers, or other road users.
Support:
03 Examples of detectable edging for pedestrians include:
- Prefabricated lightweight sections of plastic, metal, or other suitable materials that are interconnected and fixed in place to form a continuous edge.
- Prefabricated lightweight sections of plastic, metal, or other suitable materials that are interconnected, fixed in place, and placed at ground level to provide a continuous connection between channelizing devices located at intervals along the edge of the sidewalk or walkway.
- Sections of lumber interconnected and fixed in place to form a continuous edge.
- Formed-in-place asphalt or concrete curb.
- Prefabricated concrete curb sections that are interconnected and fixed in place to form a continuous edge.
- Continuous temporary traffic barrier or longitudinal channelizing barricades placed along the edge of the sidewalk or walkway that provides a pedestrian edging at ground level.
- Chain link or other fencing equipped with a continuous bottom rail.
Guidance:
04 Detectable pedestrian edging should be orange, white, or yellow and should match the color of the adjacent channelizing devices or traffic control devices, if any are present.
Section 6F.75 Temporary Raised Islands
Standard:
01 Temporary raised islands shall be used only in combination with pavement striping and other suitable channelizing devices.
Option:
02 A temporary raised island may be used to separate vehicular traffic flows in two-lane, two-way operations on roadways having a vehicular traffic volume range of 4,000 to 15,000 average daily traffic (ADT) and on freeways having a vehicular traffic volume range of 22,000 ADT to 60,000 ADT.
03 Temporary raised islands also may be used in other than two-lane, two-way operations where physical separation of vehicular traffic from the TTC zone is not required.
Guidance:
04 Temporary raised islands should have the basic dimensions of 4 inches high by at least 12 inches wide and have rounded or chamfered corners.
05 The temporary raised islands should not be designed in such a manner that they would cause a motorist to lose control of the vehicle if the vehicle inadvertently strikes the temporary raised island. If struck, pieces of the island should not be dislodged to the extent that they could penetrate the occupant compartment or involve other vehicles.
Standard:
06 At pedestrian crossing locations, temporary raised islands shall have an opening or be shortened to provide at least a 60-inch wide pathway for the crossing pedestrian.
Section 6F.76 Opposing Traffic Lane Divider and Sign (W6-4)
Support:
01 Opposing traffic lane dividers are delineation devices used as center lane dividers to separate opposing vehicular traffic on a two-lane, two-way operation.
Standard:
02 Opposing traffic lane dividers shall not be placed across pedestrian crossings.
03 The Opposing Traffic Lane Divider (W6-4) sign (see Figure 6F-4) shall be an upright, retroreflective orange-colored sign placed on a flexible support and sized at least 12 inches wide by 18 inches high.
Section 6F.77 Pavement Markings
Support:
01 Pavement markings are installed or existing markings are maintained or enhanced in TTC zones to provide road users with a clearly defined path for travel through the TTC zone in day, night, and twilight periods under both wet and dry pavement conditions.
Guidance:
02 The work should be planned and staged to provide for the placement and removal of the pavement markings in a way that minimizes the disruption to traffic flow approaching and through the TTC zone during the placement and removal process.
Standard:
03 Existing pavement markings shall be maintained in all long-term stationary (see Section 6G.02) TTC zones in accordance with Chapters 3A and 3B, except as otherwise provided for temporary pavement markings in Section 6F.78. Pavement markings shall match the alignment of the markings in place at both ends of the TTC zone. Pavement markings shall be placed along the entire length of any paved detour or temporary roadway prior to the detour or roadway being opened to road users.
04 For long-term stationary operations, pavement markings in the temporary traveled way that are no longer applicable shall be removed or obliterated as soon as practical. Pavement marking obliteration shall remove the non-applicable pavement marking material, and the obliteration method shall minimize pavement scarring. Painting over existing pavement markings with black paint or spraying with asphalt shall not be accepted as a substitute for removal or obliteration.
Option:
05 Removable, non-reflective, preformed tape that is approximately the same color as the pavement surface may be used where markings need to be covered temporarily.
Section 6F.78 Temporary Markings
Support:
01 Temporary markings are those pavement markings or devices that are placed within TTC zones to provide road users with a clearly defined path of travel through the TTC zone when the permanent markings are either removed or obliterated during the work activities. Temporary markings are typically needed during the reconstruction of a road while it is open to traffic, such as overlays or surface treatments or where lanes are temporarily shifted on pavement that is to remain in place.
Guidance:
02 Unless justified based on engineering judgment, temporary pavement markings should not remain in place for more than 14 daysafter the application of the pavement surface treatment or the construction of the final pavement surface on new roadways or over existing pavements.
03 The temporary use of edge lines, channelizing lines, lane-reduction transitions, gore markings, and other longitudinal markings, and the various non-longitudinal markings (such as stop lines, railroad crossings, crosswalks, words, symbols, or arrows) should be in accordance with the State's or highway agency's policy.
Standard:
04 Warning signs, channelizing devices, and delineation shall be used to indicate required road user paths in TTC zones where it is not possible to provide a clear path by pavement markings.
05 Except as otherwise provided in this Section, all temporary pavement markings for no-passing zones shall comply with the requirements of Chapters 3A and 3B. All temporary broken-line pavement markings shall use the same cycle length as permanent markings and shall have line segments that are at least 2 feet long.
Guidance:
06 All pavement markings and devices used to delineate road user paths should be reviewed during daytime and nighttime periods.
Option:
07 Half-cycle lengths with a minimum of 2-foot stripes may be used on roadways with severe curvature (see Section 3A.06) for broken line center lines in passing zones and for lane lines.
08 For temporary situations of 14 days or less, for a two- or three-lane road, no-passing zones may be identified by using DO NOT PASS (R4-1), PASS WITH CARE (R4-2), and NO PASSING ZONE (W14-3) signs (see Sections 2B.28, 2B.29, and 2C.45) rather than pavement markings. Also, DO NOT PASS, PASS WITH CARE, and NO PASSING ZONE signs may be used instead of pavement markings on roads with low volumes for longer periods in accordance with the State's or highway agency's policy.
Guidance:
09 If used, the DO NOT PASS, PASS WITH CARE, and NO PASSING ZONE signs should be placed in accordance with Sections 2B.28, 2B.29, and 2C.45.
10 If used, the NO CENTER LINE sign should be placed in accordance with Section 6F.47.
Section 6F.79 Temporary Raised Pavement Markers
Option:
01 Retroreflective or internally illuminated raised pavement markers, or non-retroreflective raised pavement markers supplemented by retroreflective or internally illuminated markers, may be substituted for markings of other types in TTC zones.
Standard:
02 If used, the color and pattern of the raised pavement markers shall simulate the color and pattern of the markings for which they substitute.
03 If temporary raised pavement markers are used to substitute for broken line segments, a group of at least three retroreflective markers shall be equally spaced at no greater than N/8 (see Section 3B.14). The value of N for a broken or dotted line shall equal the length of one line segment plus one gap.
04 If temporary raised pavement markers are used to substitute for solid lines, the markers shall be equally spaced at no greater than N/4, with retroreflective or internally illuminated units at a spacing no greater than N/2. The value of N referenced for solid lines shall equal the N for the broken or dotted lines that might be adjacent to or might extend the solid lines (see Section 3B.11).
Option:
05 Temporary raised pavement markers may be used to substitute for broken line segments by using at least two retroreflective markers placed at each end of a segment of 2 to 5 feet in length, using the same cycle length as permanent markings.
Guidance:
06 Temporary raised pavement markers used on 2- to 5-foot segments to substitute for broken line segments should not be in place for more than 14 days unless justified by engineering judgment.
07 Raised pavement markers should be considered for use along surfaced detours or temporary roadways, and other changed or new travel-lane alignments.
Option:
08 Retroreflective or internally illuminated raised pavement markers, or non-retroreflective raised pavement markers supplemented by retroreflective or internally illuminated markers, may also be used in TTC zones to supplement markings as prescribed in Chapters 3A and 3B.
Section 6F.80 Delineators
Standard:
01 When used, delineators shall combine with or supplement other TTC devices. They shall be mounted on crashworthy supports so that the reflecting unit is approximately 4 feet above the near roadway edge. The standard color for delineators used along both sides of two-way streets and highways and the right-hand side of one-way roadways shall be white. Delineators used along the left-hand side of one-way roadways shall be yellow.
Guidance:
02 Spacing along roadway curves should be as set forth in Section 3F.04 and should be such that several delineators are constantly visible to the driver.
Option:
03 Delineators may be used in TTC zones to indicate the alignment of the roadway and to outline the required vehicle path through the TTC zone.
Section 6F.81 Lighting Devices
Guidance:
01 Lighting devices should be provided in TTC zones based on engineering judgment.
02 When used to supplement channelization, the maximum spacing for warning lights should be identical to the channelizing device spacing requirements.
Option:
03 Lighting devices may be used to supplement retroreflectorized signs, barriers, and channelizing devices.
04 During normal daytime maintenance operations, the functions of flashing warning beacons may be provided by high-intensity rotating, flashing, oscillating, or strobe lights on a maintenance vehicle.
Standard:
05 Although vehicle hazard warning lights are permitted to be used to supplement high-intensity rotating, flashing, oscillating, or strobe lights, they shall not be used instead of high-intensity rotating, flashing, oscillating, or strobe lights.
Section 6F.82 Floodlights
Support:
01 Utility, maintenance, or construction activities on highways are frequently conducted during nighttime periods when vehicular traffic volumes are lower. Large construction projects are sometimes operated on a double-shift basis requiring night work (see Section 6G.19).
Guidance:
02 When nighttime work is being performed, floodlights should be used to illuminate the work area, equipment crossings, and other areas.
Standard:
03 Except in emergency situations, flagger stations shall be illuminated at night.
04 Floodlighting shall not produce a disabling glare condition for approaching road users, flaggers, or workers.
Guidance:
05 The adequacy of the floodlight placement and elimination of potential glare should be determined by driving through and observing the floodlighted area from each direction on all approaching roadways after the initial floodlight setup, at night, and periodically.
Support:
06 Desired illumination levels vary depending upon the nature of the task involved. An average horizontal luminance of 5 foot candles can be adequate for general activities. Tasks requiring high levels of precision and extreme care can require an average horizontal luminance of 20 foot candles.
Section 6F.83 Warning Lights
Support:
01 Type A, Type B, Type C, and Type D 360-degree warning lights are portable, powered, yellow, lens-directed, enclosed lights.
Standard:
02 Warning lights shall be in accordance with the current ITE "Purchase Specification for Flashing and Steady-Burn Warning Lights" (see Section 1A.11).
03 When warning lights are used, they shall be mounted on signs or channelizing devices in a manner that, if hit by an errant vehicle, they will not be likely to penetrate the windshield.
Guidance:
04 The maximum spacing for warning lights should be identical to the channelizing device spacing requirements.
Support:
05 The light weight and portability of warning lights are advantages that make these devices useful as supplements to the retroreflectorization on signs and channelizing devices. The flashing lights are effective in attracting road users' attention.
Option:
06 Warning lights may be used in either a steady-burn or flashing mode.
Standard:
07 Except for the sequential flashing warning lights that are described in Paragraphs 8 and 9, flashing warning lights shall not be used for delineation, as a series of flashers fails to identify the desired vehicle path.
Option:
08 A series of sequential flashing warning lights may be placed on channelizing devices that form a merging taper in order to increase driver detection and recognition of the merging taper.
Standard:
09 If a series of sequential flashing warning lights is used, the successive flashing of the lights shall occur from the upstream end of the merging taper to the downstream end of the merging taper in order to identify the desired vehicle path. Each flashing warning light in the sequence shall be flashed at a rate of not less than 55 or more than 75 times per minute.
10 Type A Low-Intensity Flashing warning lights, Type C Steady-Burn warning lights, and Type D 360-degree Steady-Burn warning lights shall be maintained so as to be capable of being visible on a clear night from a distance of 3,000 feet. Type B High-Intensity Flashing warning lights shall be maintained so as to be capable of being visible on a sunny day when viewed without the sun directly on or behind the device from a distance of 1,000 feet.
11 Warning lights shall have a minimum mounting height of 30 inches to the bottom of the lens.
Support:
12 Type A Low-Intensity Flashing warning lights are used to warn road users during nighttime hours that they are approaching or proceeding in a potentially hazardous area.
Option:
13 Type A warning lights may be mounted on channelizing devices.
Support:
14 Type B High-Intensity Flashing warning lights are used to warn road users during both daylight and nighttime hours that they are approaching a potentially hazardous area.
Option:
15 Type B warning lights are designed to operate 24 hours per day and may be mounted on advance warning signs or on independent supports.
16 Type C Steady-Burn warning lights and Type D 360-degree Steady-Burn warning lights may be used during nighttime hours to delineate the edge of the traveled way.
Guidance:
17 When used to delineate a curve, Type C and Type D 360-degree warning lights should only be used on devices on the outside of the curve, and not on the inside of the curve.
Section 6F.84 Temporary Traffic Control Signals
Standard:
01 Temporary traffic control signals (see Section 4D.32) used to control road user movements through TTC zones and in other TTC situations shall comply with the applicable provisions of Part 4.
Support:
02 Temporary traffic control signals are typically used in TTC zones such as temporary haul road crossings; temporary one-way operations along a one-lane, two-way highway; temporary one-way operations on bridges, reversible lanes, and intersections.
Standard:
03 A temporary traffic control signal that is used to control traffic through a one-lane, two-way section of roadway shall comply with the provisions of Section 4H.02.
Guidance:
04 Where pedestrian traffic is detoured to a temporary traffic control signal, engineering judgment should be used to determine if pedestrian signals or accessible pedestrian signals (see Section 4E.09) are needed for crossing along an alternate route.
05 When temporary traffic control signals are used, conflict monitors typical of traditional traffic control signal operations should be used.
Option:
06 Temporary traffic control signals may be portable or temporarily mounted on fixed supports.
Guidance:
07 Temporary traffic control signals should only be used in situations where temporary traffic control signals are preferable to other means of traffic control, such as changing the work staging or work zone size to eliminate one-way vehicular traffic movements, using flaggers to control one-way or crossing movements, using STOP or YIELD signs, and using warning devices alone.
Support:
08 Factors related to the design and application of temporary traffic control signals include the following:
- Safety and road user needs;
- Work staging and operations;
- The feasibility of using other TTC strategies (for example, flaggers, providing space for two lanes, or detouring road users, including bicyclists and pedestrians);
- Sight distance restrictions;
- Human factors considerations (for example, lack of driver familiarity with temporary traffic control signals);
- Road-user volumes including roadway and intersection capacity;
- Affected side streets and driveways;
- Vehicle speeds;
- The placement of other TTC devices;
- Parking;
- Turning restrictions;
- Pedestrians;
- The nature of adjacent land uses (such as residential or commercial);
- Legal authority;
- Signal phasing and timing requirements;
- Full-time or part-time operation;
- Actuated, fixed-time, or manual operation;
- Power failures or other emergencies;
- Inspection and maintenance needs;
- Need for detailed placement, timing, and operation records; and
- Operation by contractors or by others.
09 Although temporary traffic control signals can be mounted on trailers or lightweight portable supports, fixed supports offer superior resistance to displacement or damage by severe weather, vehicle impact, and vandalism.
Guidance:
10 Other TTC devices should be used to supplement temporary traffic control signals, including warning and regulatory signs, pavement markings, and channelizing devices.
11 Temporary traffic control signals not in use should be covered or removed.
12 If a temporary traffic control signal is located within 1/2 mile of an adjacent traffic control signal, consideration should be given to interconnected operation.
Standard:
13 Temporary traffic control signals shall not be located within 200 feet of a grade crossing unless the temporary traffic control signal is provided with preemption in accordance with Section 4D.27, or unless a uniformed officer or flagger is provided at the crossing to prevent vehicles from stopping within the crossing.
Section 6F.85 Temporary Traffic Barriers
Support:
01 Temporary traffic barriers, including shifting portable or movable barriers, are devices designed to help prevent penetration by vehicles while minimizing injuries to vehicle occupants, and to protect workers, bicyclists, and pedestrians.
02 The four primary functions of temporary traffic barriers are:
- To keep vehicular traffic from entering work areas, such as excavations or material storage sites;
- To separate workers, bicyclists, and pedestrians from motor vehicle traffic;
- To separate opposing directions of vehicular traffic; and
- To separate vehicular traffic, bicyclists, and pedestrians from the work area such as false work for bridges and other exposed objects.
Option:
03 Temporary traffic barriers may be used to separate two-way vehicular traffic.
Guidance:
04 Because the protective requirements of a TTC situation have priority in determining the need for temporary traffic barriers, their use should be based on an engineering study.
Standard:
05 Temporary traffic barriers shall be supplemented with standard delineation, pavement markings, or channelizing devices for improved daytime and nighttime visibility if they are used to channelize vehicular traffic. The delineation color shall match the applicable pavement marking color.
06 Temporary traffic barriers, including their end treatments, shall be crashworthy. In order to mitigate the effect of striking the upstream end of a temporary traffic barrier, the end shall be installed in accordance with AASHTO's "Roadside Design Guide" (see Section 1A.11) by flaring until the end is outside the acceptable clear zone or by providing crashworthy end treatments.
Option:
07 Warning lights or steady-burn lamps may be mounted on temporary traffic barrier installations.
Support:
08 Movable barriers are capable of being repositioned laterally using a transfer vehicle that travels along the barrier. Movable barriers enable short-term closures to be installed and removed on long-term projects. Providing a barrier-protected work space for short-term closures and providing unbalanced flow to accommodate changes in the direction of peak-period traffic flows are two of the advantages of using movable barriers.
09 Figure 6H-45 shows a temporary reversible lane using movable barriers. The notable feature of the movable barrier is that in both Phase A and Phase B, the lanes used by opposing traffic are separated by a barrier.
10 Figure 6H-34 shows an exterior lane closure using a temporary traffic barrier. Notes 7 though 9 address the option of using a movable barrier. By using a movable barrier, the barrier can be positioned to close the lane during the off-peak periods and can be relocated to open the lane during peak periods to accommodate peak traffic flows. With one pass of the transfer vehicle, the barrier can be moved out of the lane and onto the shoulder. Furthermore, if so desired, with a second pass of the transfer vehicle, the barrier could be moved to the roadside beyond the shoulder.
11 More specific information on the use of temporary traffic barriers is contained in Chapters 8 and 9 of AASHTO's "Roadside Design Guide" (see Section 1A.11).
Section 6F.86 Crash Cushions
Support:
01 Crash cushions are systems that mitigate the effects of errant vehicles that strike obstacles, either by smoothly decelerating the vehicle to a stop when hit head-on, or by redirecting the errant vehicle. The two types of crash cushions that are used in TTC zones are stationary crash cushions and truck-mounted attenuators. Crash cushions in TTC zones help protect the drivers from the exposed ends of barriers, fixed objects, shadow vehicles, and other obstacles. Specific information on the use of crash cushions can be found in AASHTO's "Roadside Design Guide" (see Section 1A.11).
Standard:
02 Crash cushions shall be crashworthy. They shall also be designed for each application to stop or redirect errant vehicles under prescribed conditions. Crash cushions shall be periodically inspected to verify that they have not been hit or damaged. Damaged crash cushions shall be promptly repaired or replaced to maintain their crashworthiness.
Support:
03 Stationary crash cushions are used in the same manner as permanent highway installations to protect drivers from the exposed ends of barriers, fixed objects, and other obstacles.
Standard:
04 Stationary crash cushions shall be designed for the specific application intended.
05 Truck-mounted attenuators shall be energy-absorbing devices attached to the rear of shadow trailers or trucks. If used, the shadow vehicle with the attenuator shall be located in advance of the work area, workers, or equipment to reduce the severity of rear-end crashes from errant vehicles.
Support:
06 Trucks or trailers are often used as shadow vehicles to protect workers or work equipment from errant vehicles. These shadow vehicles are normally equipped with flashing arrows, changeable message signs, and/or high-intensity rotating, flashing, oscillating, or strobe lights located properly in advance of the workers and/or equipment that they are protecting. However, these shadow vehicles might themselves cause injuries to occupants of the errant vehicles if they are not equipped with truck-mounted attenuators.
Guidance:
07 The shadow truck should be positioned a sufficient distance in advance of the workers or equipment being protected so that there will be sufficient distance, but not so much so that errant vehicles will travel around the shadow truck and strike the protected workers and/or equipment.
Support:
08 Chapter 9 of AASHTO's "Roadside Design Guide" (see Section 1A.11) contains additional information regarding the use of shadow vehicles.
Guidance:
09 If used, the truck-mounted attenuator should be used in accordance with the manufacturer's specifications.
Section 6F.87 Rumble Strips
Support:
01 Transverse rumble strips consist of intermittent, narrow, transverse areas of rough-textured or slightly raised or depressed road surface that extend across the travel lanes to alert drivers to unusual vehicular traffic conditions. Through noise and vibration they attract the driver's attention to such features as unexpected changes in alignment and to conditions requiring a stop.
02 Longitudinal rumble strips consist of a series of rough-textured or slightly raised or depressed road surfaces located along the shoulder to alert road users that they are leaving the travel lanes.
Standard:
03 If it is desirable to use a color other than the color of the pavement for a longitudinal rumble strip, the color of the rumble strip shall be the same color as the longitudinal line the rumble strip supplements.
04 If the color of a transverse rumble strip used within a travel lane is not the color of the pavement, the color of the rumble strip shall be white, black, or orange.
Option:
05 Intervals between transverse rumble strips may be reduced as the distance to the approached conditions is diminished in order to convey an impression that a closure speed is too fast and/or that an action is imminent. A sign warning drivers of the onset of rumble strips may be placed in advance of any transverse rumble strip installation.
Guidance:
06 Transverse rumble strips should be placed transverse to vehicular traffic movement. They should not adversely affect overall pavement skid resistance under wet or dry conditions.
07 In urban areas, even though a closer spacing might be warranted, transverse rumble strips should be designed in a manner that does not promote unnecessary braking or erratic steering maneuvers by road users.
08 Transverse rumble strips should not be placed on sharp horizontal or vertical curves.
09 Rumble strips should not be placed through pedestrian crossings or on bicycle routes.
10 Transverse rumble strips should not be placed on roadways used by bicyclists unless a minimum clear path of 4 feet is provided at each edge of the roadway or on each paved shoulder as described in AASHTO's "Guide to the Development of Bicycle Facilities" (see Section 1A.11).
11 Longitudinal rumble strips should not be placed on the shoulder of a roadway that is used by bicyclists unless a minimum clear path of 4 feet is also provided on the shoulder.
Section 6F.88 Screens
Support:
01 Screens are used to block the road users' view of activities that can be distracting. Screens might improve safety and motor vehicle traffic flow where volumes approach the roadway capacity because they discourage gawking and reduce headlight glare from oncoming motor vehicle traffic.
Guidance:
02 Screens should not be mounted where they could adversely restrict road user visibility and sight distance and adversely affect the reasonably safe operation of vehicles.
Option:
03 Screens may be mounted on the top of temporary traffic barriers that separate two-way motor vehicle traffic.
Guidance:
04 Design of screens should be in accordance with Chapter 9 of AASHTO's "Roadside Design Guide" (see Section 1A.11).
